The Pch2 AAA+ ATPase promotes phosphorylation of the Hop1 meiotic checkpoint adaptor in response to synaptonemal complex defects
- PMID: 27257060
- PMCID: PMC5027488
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw506
The Pch2 AAA+ ATPase promotes phosphorylation of the Hop1 meiotic checkpoint adaptor in response to synaptonemal complex defects
Abstract
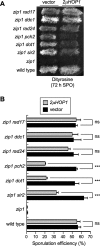
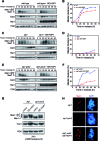
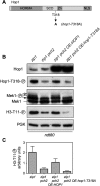
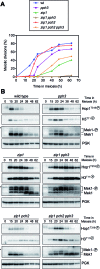
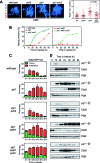
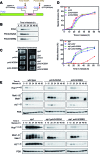
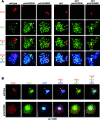
Meiotic cells possess surveillance mechanisms that monitor critical events such as recombination and chromosome synapsis. Meiotic defects resulting from the absence of the synaptonemal complex component Zip1 activate a meiosis-specific checkpoint network resulting in delayed or arrested meiotic progression. Pch2 is an evolutionarily conserved AAA+ ATPase required for the checkpoint-induced meiotic block in the zip1 mutant, where Pch2 is only detectable at the ribosomal DNA array (nucleolus). We describe here that high levels of the Hop1 protein, a checkpoint adaptor that localizes to chromosome axes, suppress the checkpoint defect of a zip1 pch2 mutant restoring Mek1 activity and meiotic cell cycle delay. We demonstrate that the critical role of Pch2 in this synapsis checkpoint is to sustain Mec1-dependent phosphorylation of Hop1 at threonine 318. We also show that the ATPase activity of Pch2 is essential for its checkpoint function and that ATP binding to Pch2 is required for its localization. Previous work has shown that Pch2 negatively regulates Hop1 chromosome abundance during unchallenged meiosis. Based on our results, we propose that, under checkpoint-inducing conditions, Pch2 also possesses a positive action on Hop1 promoting its phosphorylation and its proper distribution on unsynapsed chromosome axes.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Homeostatic Control of Meiotic Prophase Checkpoint Function by Pch2 and Hop1.Curr Biol. 2020 Nov 16;30(22):4413-4424.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.08.064. Epub 2020 Sep 10. Curr Biol. 2020. PMID: 32916108
-
Characterization of Pch2 localization determinants reveals a nucleolar-independent role in the meiotic recombination checkpoint.Chromosoma. 2019 Sep;128(3):297-316. doi: 10.1007/s00412-019-00696-7. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Chromosoma. 2019. PMID: 30859296
-
Pch2 orchestrates the meiotic recombination checkpoint from the cytoplasm.PLoS Genet. 2021 Jul 14;17(7):e1009560. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009560. eCollection 2021 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 34260586 Free PMC article.
-
Getting there: understanding the chromosomal recruitment of the AAA+ ATPase Pch2/TRIP13 during meiosis.Curr Genet. 2021 Aug;67(4):553-565. doi: 10.1007/s00294-021-01166-3. Epub 2021 Mar 12. Curr Genet. 2021. PMID: 33712914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pch2(TRIP13): controlling cell division through regulation of HORMA domains.Chromosoma. 2015 Sep;124(3):333-9. doi: 10.1007/s00412-015-0516-y. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Chromosoma. 2015. PMID: 25895724 Review.
Cited by
-
The conserved AAA ATPase PCH-2 distributes its regulation of meiotic prophase events through multiple meiotic HORMADs in C. elegans.PLoS Genet. 2023 Apr 14;19(4):e1010708. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010708. eCollection 2023 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 37058535 Free PMC article.
-
Resolvases, Dissolvases, and Helicases in Homologous Recombination: Clearing the Road for Chromosome Segregation.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jan 8;11(1):71. doi: 10.3390/genes11010071. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31936378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Replication protein-A, RPA, plays a pivotal role in the maintenance of recombination checkpoint in yeast meiosis.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 25;14(1):9550. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60082-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38664461 Free PMC article.
-
Keeping it safe: control of meiotic chromosome breakage.Trends Genet. 2025 Apr;41(4):315-329. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2024.11.006. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Trends Genet. 2025. PMID: 39672680 Review.
-
The ATPase activity of yeast chromosome axis protein Hop1 affects the frequency of meiotic crossovers.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jan 24;53(3):gkae1264. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae1264. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39727188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- MacQueen A.J., Hochwagen A. Checkpoint mechanisms: the puppet masters of meiotic prophase. Trends Cell. Biol. 2011;21:393–400. - PubMed
-
- Roeder G.S., Bailis J.M. The pachytene checkpoint. Trends Genet. 2000;16:395–403. - PubMed
-
- Schwacha A., Kleckner N. Interhomolog bias during meiotic recombination: meiotic functions promote a highly differentiated interhomolog-only pathway. Cell. 1997;90:1123–1135. - PubMed
-
- Sym M., Engebrecht J.A., Roeder G.S. ZIP1 is a synaptonemal complex protein required for meiotic chromosome synapsis. Cell. 1993;72:365–378. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

