A two-neuron system for adaptive goal-directed decision-making in Lymnaea
- PMID: 27257106
- PMCID: PMC4895806
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11793
A two-neuron system for adaptive goal-directed decision-making in Lymnaea
Abstract
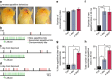
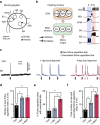
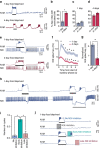
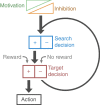
During goal-directed decision-making, animals must integrate information from the external environment and their internal state to maximize resource localization while minimizing energy expenditure. How this complex problem is solved by the nervous system remains poorly understood. Here, using a combined behavioural and neurophysiological approach, we demonstrate that the mollusc Lymnaea performs a sophisticated form of decision-making during food-searching behaviour, using a core system consisting of just two neuron types. The first reports the presence of food and the second encodes motivational state acting as a gain controller for adaptive behaviour in the absence of food. Using an in vitro analogue of the decision-making process, we show that the system employs an energy management strategy, switching between a low- and high-use mode depending on the outcome of the decision. Our study reveals a parsimonious mechanism that drives a complex decision-making process via regulation of levels of tonic inhibition and phasic excitation.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Food arousal in the pond snail, Lymnaea stagnalis.Behav Neural Biol. 1987 Sep;48(2):222-36. doi: 10.1016/s0163-1047(87)90780-1. Behav Neural Biol. 1987. PMID: 3675517
-
Multilevel inhibition of feeding by a peptidergic pleural interneuron in the mollusc Lymnaea stagnalis.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2004 May;190(5):379-90. doi: 10.1007/s00359-004-0503-x. Epub 2004 Mar 24. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15042400
-
The activity of isolated neurons and the modulatory state of an isolated nervous system represent a recent behavioural state.J Exp Biol. 2015 Apr 15;218(Pt 8):1151-8. doi: 10.1242/jeb.111930. Epub 2015 Feb 24. J Exp Biol. 2015. PMID: 25714568
-
Involvement of basal ganglia and orbitofrontal cortex in goal-directed behavior.Prog Brain Res. 2000;126:193-215. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(00)26015-9. Prog Brain Res. 2000. PMID: 11105648 Review.
-
Neural systems analysis of decision making during goal-directed navigation.Prog Neurobiol. 2012 Jan;96(1):96-135. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2011.08.010. Epub 2011 Sep 21. Prog Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 21964237 Review.
Cited by
-
Proactive and retroactive interference with associative memory consolidation in the snail Lymnaea is time and circuit dependent.Commun Biol. 2019 Jun 26;2:242. doi: 10.1038/s42003-019-0470-y. eCollection 2019. Commun Biol. 2019. PMID: 31263786 Free PMC article.
-
Satiation level affects anti-predatory decisions in foraging juvenile crayfish.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2017 Mar;203(3):223-232. doi: 10.1007/s00359-017-1158-8. Epub 2017 Feb 28. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28247016
-
A central control circuit for encoding perceived food value.Sci Adv. 2018 Nov 21;4(11):eaau9180. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aau9180. eCollection 2018 Nov. Sci Adv. 2018. PMID: 30474061 Free PMC article.
-
Functional mapping of the molluscan brain guided by synchrotron X-ray tomography.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Mar 4;122(9):e2422706122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2422706122. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40014565 Free PMC article.
-
Impairment of the serotonergic neurons underlying reinforcement elicits extinction of the repeatedly reactivated context memory.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 14;6:36933. doi: 10.1038/srep36933. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27841309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gold J. I. & Shadlen M. N. The neural basis of decision making. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 30, 535–574 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Rangel A. & Hare T. Neural computations associated with goal-directed choice. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 20, 262–270 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Staras K., Kemenes I., Benjamin P. R. & Kemenes G. Loss of self-inhibition is a cellular mechanism for episodic rhythmic behavior. Curr. Biol. 13, 116–124 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

