Skeletal muscle diffusion tensor-MRI fiber tracking: rationale, data acquisition and analysis methods, applications and future directions
- PMID: 27257975
- PMCID: PMC5136336
- DOI: 10.1002/nbm.3563
Skeletal muscle diffusion tensor-MRI fiber tracking: rationale, data acquisition and analysis methods, applications and future directions
Abstract
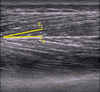
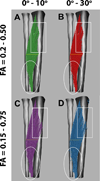
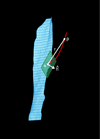
The mechanical functions of muscles involve the generation of force and the actuation of movement by shortening or lengthening under load. These functions are influenced, in part, by the internal arrangement of muscle fibers with respect to the muscle's mechanical line of action. This property is known as muscle architecture. In this review, we describe the use of diffusion tensor (DT)-MRI muscle fiber tracking for the study of muscle architecture. In the first section, the importance of skeletal muscle architecture to function is discussed. In addition, traditional and complementary methods for the assessment of muscle architecture (brightness-mode ultrasound imaging and cadaver analysis) are presented. Next, DT-MRI is introduced and the structural basis for the reduced and anisotropic diffusion of water in muscle is discussed. The third section discusses issues related to the acquisition of skeletal muscle DT-MRI data and presents recommendations for optimal strategies. The fourth section discusses methods for the pre-processing of DT-MRI data, the available approaches for the calculation of the diffusion tensor and the seeding and propagating of fiber tracts, and the analysis of the tracking results to measure structural properties pertinent to muscle biomechanics. Lastly, examples are presented of how DT-MRI fiber tracking has been used to provide new insights into how muscles function, and important future research directions are highlighted. Copyright © 2016 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Keywords: diffusion MRI; muscle architecture; muscle mechanics; non-invasive; skeletal muscle.
Copyright © 2016 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Aquin L, Lechner AJ, Sillau AH, Banchero N. Analysis of the shape changes of muscle fiber cross sections in guinea pigs raised at 22 degrees C and 5 degrees C. Pflugers Arch. 1980;385(3):223–228. - PubMed
-
- Polgar J, Johnson MA, Weightman D, Appleton D. Data on fibre size in thirty-six human muscles: An autopsy study. J Neurol Sci. 1973;19(3):307–318. - PubMed
-
- Landis CS, Li X, Telang FW, Molina PE, Palyka I, Vetek G, Springer CS., Jr Equilibrium transcytolemmal water-exchange kinetics in skeletal muscle in vivo. Magn Reson Med. 1999;42(3):467–478. - PubMed
-
- Trotter JA, Purslow PP. Functional morphology of the endomysium in series fibered muscles. J Morphol. 1992;212(2):109–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

