Overexpression of PIN1 Enhances Cancer Growth and Aggressiveness with Cyclin D1 Induction in EBV-Associated Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
- PMID: 27258148
- PMCID: PMC4892693
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156833
Overexpression of PIN1 Enhances Cancer Growth and Aggressiveness with Cyclin D1 Induction in EBV-Associated Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a peculiar Epstein Barr virus (EBV)-associated malignancy that is prevalent in South-East Asia. Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1 (PIN1) isomerizes specific phosphorylated amino acid residues, which makes it an important regulator in cell survival and apoptosis. In this study, we investigated the contribution made by PIN1 in NPC tumorigenesis and PIN1's potential role as a therapeutic target.
Methods: The expression of PIN1 was examined in a panel of NPC cell lines, xenografts and primary tumors. The functional roles of PIN1 in NPC cells were elucidated by the knockdown and overexpression of PIN1 in in vitro and in vivo nude mice models by siRNA and lenti-viral transfection, respectively. The antitumor effects of the PIN1 inhibitor Juglone in NPC cells were also evaluated.
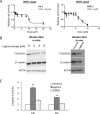
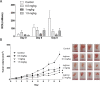
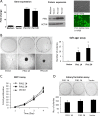
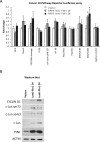
Results: We revealed the consistent overexpression of PIN1 in almost all EBV-associated NPC cell lines, xenografts and primary tumors. PIN1 suppression was capable of inhibiting cyclin D1 expression and activating caspase-3 in NPC cells. It positively regulated NPC cell proliferation, colony formation and anchorage-independent growth. The inhibition of PIN1 suppressed tumor growth in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates the oncogenic role of PIN1 in NPC tumorigenesis, and shows that its overexpression can enhance tumor cell growth via the upregulation of cyclinD1. Our findings inform the development of novel treatments targeting PIN1 for NPC patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
The protein level and transcription activity of activating transcription factor 1 is regulated by prolyl isomerase Pin1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Dec 29;7(12):e2571. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.349. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 28032861 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-183 suppresses cancer stem-like cell properties in EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2016 Jul 19;16:495. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2525-5. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27431799 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of lytic cycle of Epstein-Barr virus by suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid leads to apoptosis and tumor growth suppression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Int J Cancer. 2012 Oct 15;131(8):1930-40. doi: 10.1002/ijc.27439. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Int J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22261816
-
EBV Infection and Glucose Metabolism in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1018:75-90. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-5765-6_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29052133 Review.
-
Understanding the role of PIN1 in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Dec 7;22(45):9921-9932. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i45.9921. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 28018099 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction between Peptidyl-prolyl Cis-trans Isomerase NIMA-interacting 1 and GTP-H-Ras: Implications for Aggressiveness of Human Mammary Epithelial Cells and Drug Resistance.J Cancer Prev. 2020 Dec 30;25(4):234-243. doi: 10.15430/JCP.2020.25.4.234. J Cancer Prev. 2020. PMID: 33409256 Free PMC article.
-
Functional PIN1 promoter polymorphisms associated with risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Southern Chinese populations.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 4;7(1):4593. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04156-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28676695 Free PMC article.
-
The role of CDC25C in cell cycle regulation and clinical cancer therapy: a systematic review.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Jun 3;20:213. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01304-w. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 32518522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prolyl Isomerase Pin1 in Human Cancer: Function, Mechanism, and Significance.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Mar 31;8:168. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00168. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32296699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Cellular Functions of ATR for Therapeutic Targeting: Embryogenesis to Tumorigenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 20;24(14):11684. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411684. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511442 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lo KW, To KF, Huang DP. Focus on nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer cell. 2004;5(5):423–8. Epub 2004/05/18. . - PubMed
-
- Lo KW, Huang DP. Genetic and epigenetic changes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Seminars in cancer biology. 2002;12(6):451–62. Epub 2002/11/27. . - PubMed
-
- Lu KP. Prolyl isomerase Pin1 as a molecular target for cancer diagnostics and therapeutics. Cancer cell. 2003;4(3):175–80. Epub 2003/10/03. . - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

