Insights into the Stress Response Triggered by Kasugamycin in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 27258317
- PMCID: PMC4929434
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics5020019
Insights into the Stress Response Triggered by Kasugamycin in Escherichia coli
Abstract
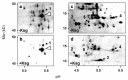
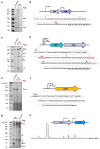
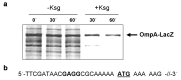
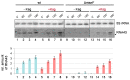
The bacteriostatic aminoglycoside antibiotic kasugamycin inhibits protein synthesis at an initial step without affecting translation elongation. It binds to the mRNA track of the ribosome and prevents formation of the translation initiation complex on canonical mRNAs. In contrast, translation of leaderless mRNAs continues in the presence of the drug in vivo. Previously, we have shown that kasugamycin treatment in E. coli stimulates the formation of protein-depleted ribosomes that are selective for leaderless mRNAs. Here, we provide evidence that prolonged kasugamycin treatment leads to selective synthesis of specific proteins. Our studies indicate that leaderless and short-leadered mRNAs are generated by different molecular mechanisms including alternative transcription and RNA processing. Moreover, we provide evidence for ribosome heterogeneity in response to kasugamycin treatment by alteration of the modification status of the stalk proteins bL7/L12.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; kasugamycin; leaderless mRNA; translation initiation.
Figures

References
-
- Poldermans B., Goosen N., Van Knippenberg P.H. Studies on the function of two adjacent N6,N6-dimethyladenosines near the 3′ end of 16 S ribosomal RNA of Escherichia coli. I. The effect of kasugamycin on initiation of protein synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1979;254:9085–9089. - PubMed
-
- Schluenzen F., Takemoto C., Wilson D.N., Kaminishi T., Harms J.M., Hanawa-Suetsugu K., Szaflarski W., Kawazoe M., Shirouzu M., Nierhaus K.H., et al. The antibiotic kasugamycin mimics mRNA nucleotides to destabilize tRNA binding and inhibit canonical translation initiation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006;13:871–878. doi: 10.1038/nsmb1145. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

