Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis Overlap Syndrome in Patients With Biopsy-Proven Glomerulonephritis
- PMID: 27258503
- PMCID: PMC4900711
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003748
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis Overlap Syndrome in Patients With Biopsy-Proven Glomerulonephritis
Abstract
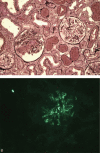
The aim of the study was to report the clinical, biological, and pathological characteristics of patients with glomerulonephritis (GN) secondary to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)/antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) overlap syndrome.A nationwide survey was conducted to identify cases of SLE/AAV overlap syndrome. Data were collected from SLE and AAV French research groups. Inclusion criteria were diagnosis of both SLE and AAV according to international classification criteria and biopsy-proven GN between 1995 and 2014. Additional cases were identified through a systematic literature review. A cohort of consecutive biopsy-proven GN was used to study the prevalence of overlapping antibodies and/or overlap syndrome.The national survey identified 8 cases of SLE/AAV overlap syndrome. All patients were female; median age was 40 years. AAV occurred before SLE (n = 3), after (n = 3), or concomitantly (n = 2). Six patients had rapidly progressive GN and 3/8 had alveolar hemorrhage. All patients had antinuclear antibodies (ANA); 7/8 had p-ANCA antimyeloperoxidase (MPO) antibodies. Renal biopsies showed lupus nephritis (LN) or pauci-immune GN. Remission was obtained in 4/8 patients. A literature review identified 31 additional cases with a similarly severe presentation. In the GN cohort, ANCA positivity was found in 30% of LN, ANA positivity in 52% of pauci-immune GN, with no correlation with pathological findings. The estimated prevalence for SLE/AAV overlap syndrome was 2/101 (2%).In patients with GN, SLE/AAV overlap syndrome may occur but with a low prevalence. Most patients have an aggressive renal presentation, with usually both ANA and anti-MPO antibodies. Further studies are needed to assess shared pathogenesis and therapeutic options.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis due to systemic lupus erythematosus and ANCA-associated vasculitis overlap.Lupus. 2020 Jul;29(8):983-986. doi: 10.1177/0961203320920368. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Lupus. 2020. PMID: 32316845
-
Vasculitis and crescentic glomerulonephritis in a newly established congenic mouse strain derived from ANCA-associated vasculitis-prone SCG/Kj mice.Autoimmunity. 2019 Aug-Sep;52(5-6):208-219. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2019.1658191. Epub 2019 Sep 2. Autoimmunity. 2019. PMID: 31476889
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus and antineutrophilic cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis overlap syndrome complicated by subarachnoid hemorrhage: case-based review.Rheumatol Int. 2018 Dec;38(12):2329-2335. doi: 10.1007/s00296-018-4169-z. Epub 2018 Oct 16. Rheumatol Int. 2018. PMID: 30327865 Review.
-
Microscopic polyangiitis in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus: a unique presentation of pulmonary-renal syndrome and case report of an overlap syndrome.CEN Case Rep. 2025 Aug;14(4):534-541. doi: 10.1007/s13730-024-00949-0. Epub 2024 Dec 11. CEN Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 39661284 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus and antineutrocytic cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis overlap syndrome presenting mainly with alveolar hemorrhage: A case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Dec 1;102(48):e36356. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036356. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 38050315 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis and lupus nephritis following COVID-19 vaccination: a case report and literature review.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 8;14:1298622. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1298622. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38299140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pauci-immune crescentic glomerulonephritis caused to dilemma in a patient with suspected systemic lupus erythematosus: a case report.CEN Case Rep. 2024 Jun;13(3):174-180. doi: 10.1007/s13730-023-00825-3. Epub 2023 Oct 14. CEN Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 37837535 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) and Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis (AAV) Overlap Syndrome: Case Report and Review of the Literature.Case Rep Rheumatol. 2019 Jan 6;2019:5013904. doi: 10.1155/2019/5013904. eCollection 2019. Case Rep Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 30723567 Free PMC article.
-
A Case of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus/Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis Overlap Syndrome with Dissociated Pathological and Immunological Findings.Case Rep Nephrol. 2020 May 15;2020:5698708. doi: 10.1155/2020/5698708. eCollection 2020. Case Rep Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32509365 Free PMC article.
-
Coincidence of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: A Case Report with Perforation of Nasal Septum and Palate.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Dec 6;16:5949-5957. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S434178. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 38084107 Free PMC article.
References
-
- D’Cruz DP, Khamashta MA, Hughes GR. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet 2007; 369:587–596. - PubMed
-
- Cervera R, Khamashta MA, Font J, et al. Morbidity and mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus during a 10-year period: a comparison of early and late manifestations in a cohort of 1,000 patients. Medicine 2003; 82:299–308. - PubMed
-
- Maroz N, Segal MS. Lupus nephritis and end-stage kidney disease. Am J Med Sci 2013; 346:319–323. - PubMed
-
- Ramos-Casals M, Nardi N, Lagrutta M, et al. Vasculitis in systemic lupus erythematosus: prevalence and clinical characteristics in 670 patients. Medicine 2006; 85:95–104. - PubMed
-
- Weening JJ, D’Agati VD, Schwartz MM, et al. The classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. Kidney Int 2004; 65:521–530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

