Safety and Efficacy of Endoscopic Therapy for Nonmalignant Duodenal Duplication Cysts: Case Report and Comprehensive Review of 28 Cases Reported in the Literature
- PMID: 27258515
- PMCID: PMC4900723
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003799
Safety and Efficacy of Endoscopic Therapy for Nonmalignant Duodenal Duplication Cysts: Case Report and Comprehensive Review of 28 Cases Reported in the Literature
Abstract
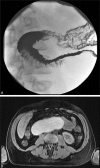
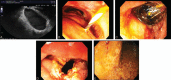
Analyze efficacy, safety of endoscopic therapy for duodenal duplication cysts (DDC) by comprehensively reviewing case reports.Tandem, independent, systematic, computerized, literature searches were performed via PubMed using medical subject headings or Keywords "cyst" and "duodenal" and "duplication"; or "cyst", and "endoscopy" or "endoscopic", and "therapy" or "decompression"; with reconciliation of generated references by two experts. Case report followed CARE guidelines.Literature review revealed 28 cases (mean = 1.3 ± 1.2 cases/report). Endoscopic therapy is increasingly reported recently (1984-1999: 3 cases, 2000-2015: 25 cases, P = 0.003, OR = 8.33, 95%-CI: 1.77-44.5). Fourteen (54%) of 26 patients were men (unknown-sex = 2). Mean age = 32.2 ± 18.3 years old. Procedure indications: acute pancreatitis-16, abdominal pain-8, jaundice-2, gastrointestinal (GI) obstruction-1, asymptomatic cyst-1. Mean maximal DDC dimension = 3.20 ± 1.53 cm (range, 1-6.5 cm). Endoscopic techniques included cyst puncture via needle knife papillotomy (NKP)/papillotome-18, snare resection of cyst-7, cystotome-2, and cyst needle aspiration/ligation-1. Endoscopic therapy was successful in all cases. Among 24 initially symptomatic patients, all remained asymptomatic post-therapy without relapses (mean follow-up = 36.5 ± 48.6 months, 3 others reported asymptomatic at follow-up of unknown duration; 1 initially asymptomatic patient remained asymptomatic 3 years post-therapy). Two complications occurred: mild intraprocedural duodenal bleeding related to NKP and treated locally endoscopically.A patient is reported who presented with vomiting, 15-kg-weight-loss, and profound dehydration for 1 month from extrinsic compression of duodenum by 14 × 6 cm DDC, underwent successful endosonographic cyst decompression with large fenestration of cyst and endoscopic aspiration of 1 L of fluid from cyst with rapid relief of symptoms. At endoscopy the DDC was intubated and visualized and random endoscopic mucosal biopsies were obtained to help exclude malignant or dysplastic DDC.Study limitations include retrospective literature review, potential reporting bias, limited patient number, variable follow-up.In conclusion, endoscopic therapy for DDC was efficacious in all 29 reported patients including current case, including patients presenting acutely with acute pancreatitis, or GI obstruction. Complications were rare and minor, suggesting that endoscopic therapy may be a useful alternative to surgery for nonmalignant DDC when performed by expert endoscopists.
Conflict of interest statement
This paper does not discuss any confidential pharmaceutical industry data reviewed by Dr. Cappell as a consultant for the United States Food & Drug Administration (FDA) Advisory Committee on Gastrointestinal Drugs. Dr. Cappell is a speaker for Movantik, a drug jointly manufactured by AstraZeneca and Daiichi Sankyo. This work does not discuss any drug or medical device manufactured or marketed by AstraZeneca or Daiichi Sankyo.The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose
Figures
References
-
- Stringer MD, Spitz L, Abel R, et al. Management of alimentary tract duplication in children. Br J Surg 1995; 82:74–78. - PubMed
-
- Destruys L, Guinard-Samuel V, Peycelon M, et al. Duodenal duplication cyst causing acute obstructive pancreatitis in a young girl with Crohn disease [Article in French]. Arch Pediatr 2014; 21:532–534. - PubMed
-
- Martínez-Alcalá García F, Peréz Pozo JM, Martínez-Alcalá García A, et al. Duodenal duplication cyst and its endoscopic resolution [Article in Spanish]. Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014; 37:274–275. - PubMed
-
- Chen JJ, Lee HC, Yeung CY, et al. Meta-analysis: the clinical features of the duodenal duplication cyst. J Pediatr Surg 2010; 45:1598–1606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

