The long noncoding RNA NRF regulates programmed necrosis and myocardial injury during ischemia and reperfusion by targeting miR-873
- PMID: 27258785
- PMCID: PMC4947670
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2016.28
The long noncoding RNA NRF regulates programmed necrosis and myocardial injury during ischemia and reperfusion by targeting miR-873
Abstract
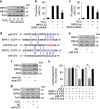
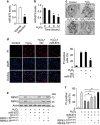
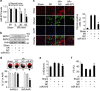
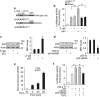
Emerging evidences suggest that necrosis is programmed and is one of the main forms of cell death in the pathological process in cardiac diseases. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are emerging as new players in gene regulation. However, it is not yet clear whether lncRNAs can regulate necrosis in cardiomyocytes. Here, we report that a long noncoding RNA, named necrosis-related factor (NRF), regulates cardiomyocytes necrosis by targeting miR-873 and RIPK1 (receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1)/RIPK3 (receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 3). Our results show that RIPK1 and RIPK3 participate in H2O2-induced cardiomyocytes necrosis. miR-873 suppresses the translation of RIPK1/RIPK3 and inhibits RIPK1/RIPK3-mediated necrotic cell death in cardiomyocytes. miR-873 reduces myocardial infarct size upon ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury in the animal model. In exploring the molecular mechanism by which miR-873 expression is regulated, we identify NRF as an endogenous sponge RNA and repress miR-873 expression. NRF directly binds to miR-873 and regulates RIPK1/RIPK3 expression and necrosis. Knockdown of NRF antagonizes necrosis in cardiomyocytes and reduces necrosis and myocardial infarction upon I/R injury. Further, we identify that p53 transcriptionally activates NRF expression. P53 regulates cardiomyocytes necrosis and myocardial I/R injury through NRF and miR-873.Our results identify a novel mechanism involving NRF and miR-873 in regulating programmed necrosis in the heart and suggest a potential therapeutic avenue for cardiovascular diseases.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-103/107 Regulate Programmed Necrosis and Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through Targeting FADD.Circ Res. 2015 Jul 31;117(4):352-63. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.305781. Epub 2015 Jun 2. Circ Res. 2015. PMID: 26038570
-
MicroRNA-24-3p Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Suppressing RIPK1 Expression in Mice.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(1):46-62. doi: 10.1159/000495161. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30439713
-
The Long Non-Coding RNA SNHG1 Attenuates Cell Apoptosis by Regulating miR-195 and BCL2-Like Protein 2 in Human Cardiomyocytes.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(3):1029-1040. doi: 10.1159/000494514. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30355909
-
Insight into long noncoding RNA-miRNA-mRNA axes in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: the implications for mechanism and therapy.Epigenomics. 2019 Nov 1;11(15):1733-1748. doi: 10.2217/epi-2019-0119. Epub 2019 Nov 8. Epigenomics. 2019. PMID: 31701757 Review.
-
RIPK1 and RIPK3: critical regulators of inflammation and cell death.Trends Cell Biol. 2015 Jun;25(6):347-53. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2015.01.001. Epub 2015 Feb 4. Trends Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25662614 Review.
Cited by
-
The lncRNA ROR/miR-124-3p/TRAF6 axis regulated the ischaemia reperfusion injury-induced inflammatory response in human cardiac myocytes.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2019 Dec;51(6):381-392. doi: 10.1007/s10863-019-09812-9. Epub 2019 Nov 25. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2019. PMID: 31768721
-
Non-Coding RNAs: Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment in Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 1;23(5):2728. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052728. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles of non-coding RNAs in cardiac regenerative medicine.Noncoding RNA Res. 2017 Jun 7;2(2):100-110. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2017.06.001. eCollection 2017 Jun. Noncoding RNA Res. 2017. PMID: 30159427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species and Lytic Programmed Cell Death in Acute Inflammation.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023 Oct;39(10-12):708-727. doi: 10.1089/ars.2022.0209. Epub 2023 Aug 31. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023. PMID: 37450339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long Non-Coding RNAs in Cardiovascular Diseases: Potential Function as Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets of Exercise Training.Noncoding RNA. 2021 Oct 11;7(4):65. doi: 10.3390/ncrna7040065. Noncoding RNA. 2021. PMID: 34698215 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cho YS, Park SY, Shin HS, Chan FK. Physiological consequences of programmed necrosis, an alternative form of cell demise. Mol Cells 2010; 29: 327–332. - PubMed
-
- Lamkanfi M, Festjens N, Declercq W, Vanden Berghe T, Vandenabeele P. Caspases in cell survival, proliferation and differentiation. Cell Death Differ 2007; 14: 44–55. - PubMed
-
- Nakagawa T, Shimizu S, Watanabe T, Yamaguchi O, Otsu K, Yamagata H et al. Cyclophilin d-dependent mitochondrial permeability transition regulates some necrotic but not apoptotic cell death. Nature 2005; 434: 652–658. - PubMed
-
- Baines CP, Kaiser RA, Purcell NH, Blair NS, Osinska H, Hambleton MA et al. Loss of cyclophilin d reveals a critical role for mitochondrial permeability transition in cell death. Nature 2005; 434: 658–662. - PubMed
-
- Oerlemans MI, Liu J, Arslan F, den Ouden K, van Middelaar BJ, Doevendans PA et al. Inhibition of rip1-dependent necrosis prevents adverse cardiac remodeling after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion in vivo. Basic Res Cardiol 2012; 107: 270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

