The effect of dimethyl sulfoxide on the induction of DNA strand breaks in plasmid DNA and colony formation of PC Cl3 mammalian cells by alpha-, beta-, and Auger electron emitters (223)Ra, (188)Re, and (99m)Tc
- PMID: 27259575
- PMCID: PMC4893047
- DOI: 10.1186/s13550-016-0203-x
The effect of dimethyl sulfoxide on the induction of DNA strand breaks in plasmid DNA and colony formation of PC Cl3 mammalian cells by alpha-, beta-, and Auger electron emitters (223)Ra, (188)Re, and (99m)Tc
Abstract
Background: DNA damage occurs as a consequence of both direct and indirect effects of ionizing radiation. The severity of DNA damage depends on the physical characteristics of the radiation quality, e.g., the linear energy transfer (LET). There are still contrary findings regarding direct or indirect interactions of high-LET emitters with DNA. Our aim is to determine DNA damage and the effect on cellular survival induced by (223)Ra compared to (188)Re and (99m)Tc modulated by the radical scavenger dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
Methods: Radioactive solutions of (223)Ra, (188)Re, or (99m)Tc were added to either plasmid DNA or to PC Cl3 cells in the absence or presence of DMSO. Following irradiation, single strand breaks (SSB) and double strand breaks (DSB) in plasmid DNA were analyzed by gel electrophoresis. To determine the radiosensitivity of the rat thyroid cell line (PC Cl3), survival curves were performed using the colony formation assay.
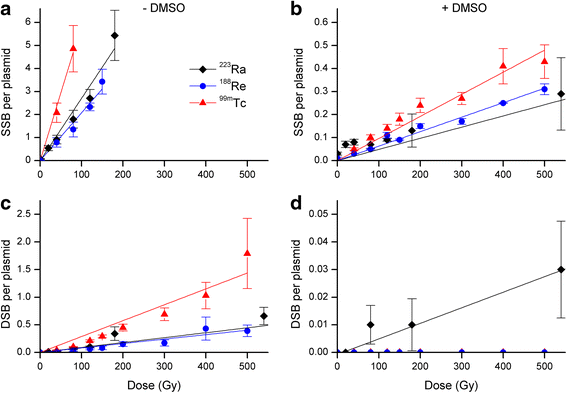
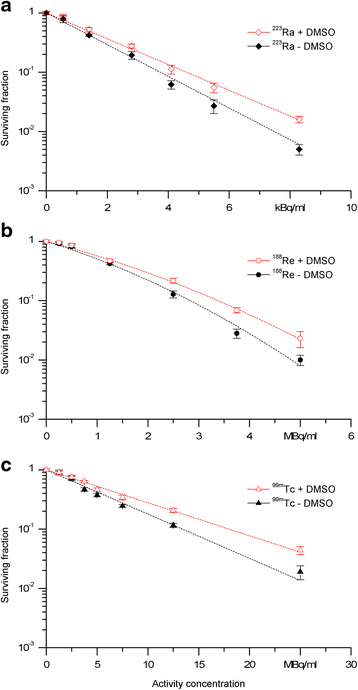
Results: Exposure to 120 Gy of (223)Ra, (188)Re, or (99m)Tc leads to maximal yields of SSB (80 %) in plasmid DNA. Irradiation with 540 Gy (223)Ra and 500 Gy (188)Re or (99m)Tc induced 40, 28, and 64 % linear plasmid conformations, respectively. DMSO prevented the SSB and DSB in a similar way for all radionuclides. However, with the α-emitter (223)Ra, a low level of DSB could not be prevented by DMSO. Irradiation of PC Cl3 cells with (223)Ra, (188)Re, and (99m)Tc pre-incubated with DMSO revealed enhanced survival fractions (SF) in comparison to treatment without DMSO. Protection factors (PF) were calculated using the fitted survival curves. These factors are 1.23 ± 0.04, 1.20 ± 0.19, and 1.34 ± 0.05 for (223)Ra, (188)Re, and (99m)Tc, respectively.
Conclusions: For (223)Ra, as well as for (188)Re and (99m)Tc, dose-dependent radiation effects were found applicable for plasmid DNA and PC Cl3 cells. The radioprotection by DMSO was in the same range for high- and low-LET emitter. Overall, the results indicate the contribution of mainly indirect radiation effects for each of the radionuclides regarding DNA damage and cell survival. In summary, our findings may contribute to fundamental knowledge about the α-particle induced DNA damage.
Keywords: Cellular survival; DMSO; LET; Plasmid DNA; α-emitter.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

