Histamine induces microglia activation and dopaminergic neuronal toxicity via H1 receptor activation
- PMID: 27260166
- PMCID: PMC4893260
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-016-0600-0
Histamine induces microglia activation and dopaminergic neuronal toxicity via H1 receptor activation
Abstract
Background: Histamine is an amine widely known as a peripheral inflammatory mediator and as a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Recently, it has been suggested that histamine acts as an innate modulator of microglial activity. Herein, we aimed to disclose the role of histamine in microglial phagocytic activity and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and to explore the consequences of histamine-induced neuroinflammation in dopaminergic (DA) neuronal survival.
Methods: The effect of histamine on phagocytosis was assessed both in vitro by using a murine N9 microglial cell line and primary microglial cell cultures and in vivo. Cells were exposed to IgG-opsonized latex beads or phosphatidylserine (PS) liposomes to evaluate Fcγ or PS receptor-mediated microglial phagocytosis, respectively. ROS production and protein levels of NADPH oxidases and Rac1 were assessed as a measure of oxidative stress. DA neuronal survival was evaluated in vivo by counting the number of tyrosine hydroxylase-positive neurons in the substantia nigra (SN) of mice.
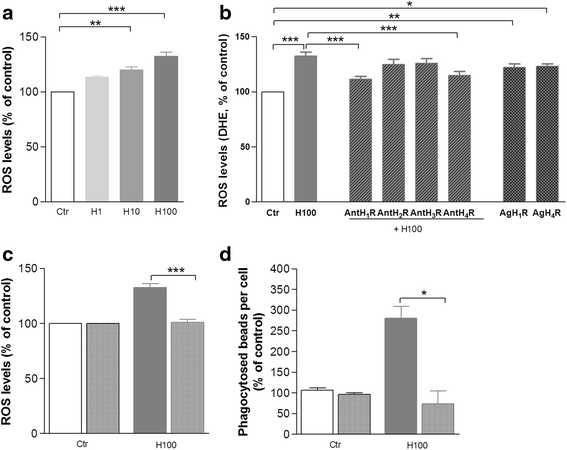
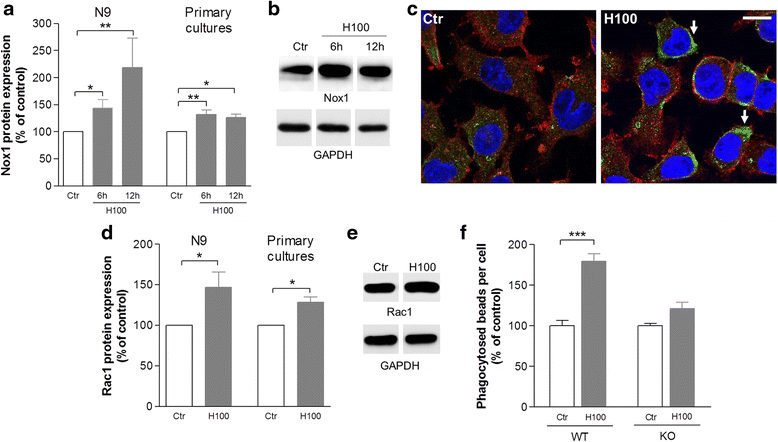
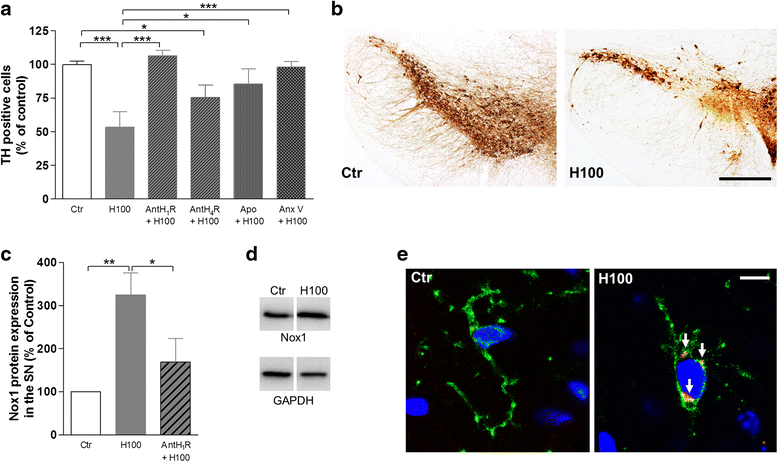
Results: We found that histamine triggers microglial phagocytosis via histamine receptor 1 (H1R) activation and ROS production via H1R and H4R activation. By using apocynin, a broad NADPH oxidase (Nox) inhibitor, and Nox1 knockout mice, we found that the Nox1 signaling pathway is involved in both phagocytosis and ROS production induced by histamine in vitro. Interestingly, both apocynin and annexin V (used as inhibitor of PS-induced phagocytosis) fully abolished the DA neurotoxicity induced by the injection of histamine in the SN of adult mice in vivo. Blockade of H1R protected against histamine-induced Nox1 expression and death of DA neurons in vivo.
Conclusions: Overall, our results highlight the relevance of histamine in the modulation of microglial activity that ultimately may interfere with neuronal survival in the context of Parkinson's disease (PD) and, eventually, other neurodegenerative diseases which are accompanied by microglia-induced neuroinflammation. Importantly, our results also open promising new perspectives for the therapeutic use of H1R antagonists to treat or ameliorate neurodegenerative processes.
Keywords: Dopaminergic neurons; Histamine; Microglia; NADPH oxidase; Neurotoxicity; Phagocytosis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ultrafine carbon particles promote rotenone-induced dopamine neuronal loss through activating microglial NADPH oxidase.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017 May 1;322:51-59. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2017.03.005. Epub 2017 Mar 7. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28283350
-
Apocyanin, a Microglial NADPH Oxidase Inhibitor Prevents Dopaminergic Neuronal Degeneration in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Parkinson's Disease Model.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Jul;53(5):3326-3337. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9267-2. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26081143
-
Neurotoxic activation of microglia is promoted by a nox1-dependent NADPH oxidase.J Neurosci. 2008 Nov 12;28(46):12039-51. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3568-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19005069 Free PMC article.
-
Dual role of histamine on microglia-induced neurodegeneration.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017 Mar;1863(3):764-769. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.12.016. Epub 2017 Jan 2. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017. PMID: 28057587 Review.
-
Chronic microglial activation and progressive dopaminergic neurotoxicity.Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Nov;35(Pt 5):1127-32. doi: 10.1042/BST0351127. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 17956294 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuronal Cell Death.Physiol Rev. 2018 Apr 1;98(2):813-880. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00011.2017. Physiol Rev. 2018. PMID: 29488822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Literature-Based Discovery Predicts Antihistamines Are a Promising Repurposed Adjuvant Therapy for Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 2;24(15):12339. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512339. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569714 Free PMC article.
-
Mast cell-mediated immune regulation in health and disease.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Aug 17;10:1213320. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1213320. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37663654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglial Phagocytosis and Its Regulation: A Therapeutic Target in Parkinson's Disease?Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Apr 27;11:144. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00144. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29755317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clear Skies, Cloudy Mind: Probiotic-Related Brain Fogginess in a Commercial Airline Pilot.Cureus. 2024 Aug 8;16(8):e66426. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66426. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39247007 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Watanabe T, Taguchi Y, Shiosaka S, Tanaka J, Kubota H, Terano Y, Tohyama M, Wada H. Distribution of the histaminergic neuron system in the central nervous system of rats; a fluorescent immunohistochemical analysis with histidine decarboxylase as a marker. Brain Res. 1984;295:13–25. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90811-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

