Co-morbidities, complications and causes of death among people with femoral neck fracture - a three-year follow-up study
- PMID: 27260196
- PMCID: PMC4893237
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-016-0291-5
Co-morbidities, complications and causes of death among people with femoral neck fracture - a three-year follow-up study
Abstract
Background: The poor outcome after a hip fracture is not fully understood. The aim of the study was to describe the prevalence of co-morbidities, complications and causes of death and to investigate factors that are able to predict mortality in old people with femoral neck fracture.
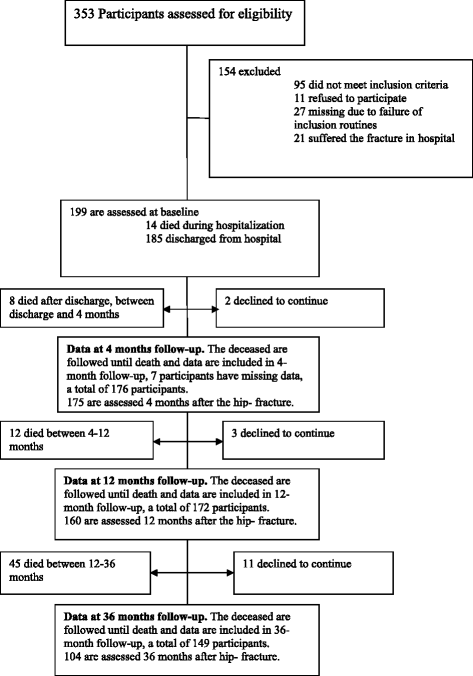
Methods: Data was obtained from a randomized, controlled trial with a 3-year follow-up at Umeå University Hospital, Sweden, which included 199 consecutive patients with femoral neck fracture, aged ≥70 years. The participants were assessed during hospitalization and in their homes 4, 12 and 36 months after surgery. Medical records and death certificates were analysed.
Results: Multivariate analysis revealed that cancer, dependence in P-ADL (Personal Activities of Daily Living), cardiovascular disease, dementia at baseline or pulmonary emboli or cardiac failure during hospitalization were all independent predictors of 3-year mortality. Seventy-nine out of 199 participants (40 %) died within 3 years. Cardiovascular events (24 %), dementia (23 %), hip-fracture (19 %) and cancer (13 %) were the most common primary causes of death. In total, 136 participants suffered at least one urinary tract infection; 114 suffered 542 falls and 37 sustained 56 new fractures, including 13 hip fractures, during follow-up.
Conclusion: Old people with femoral neck fracture have multiple co-morbidities and suffer numerous complications. Thus randomized intervention studies should focus on prevention of complications that might be avoidable such as infections, heart diseases, falls and fractures.
Keywords: Cause of death; Complications; Hip fracture.
Figures
References
-
- Mak JC, Cameron ID, March LM. Evidence-based guidelines for the management of hip fractures in older persons: an update. Med J Aust. 2010;192:37–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical