FR-900098, an antimalarial development candidate that inhibits the non-mevalonate isoprenoid biosynthesis pathway, shows no evidence of acute toxicity and genotoxicity
- PMID: 27260413
- PMCID: PMC4991342
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2016.1195537
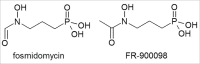
FR-900098, an antimalarial development candidate that inhibits the non-mevalonate isoprenoid biosynthesis pathway, shows no evidence of acute toxicity and genotoxicity
Abstract
FR-900098 is an inhibitor of 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate (DXP) reductoisomerase, the second enzyme in the non-mevalonate isoprenoid biosynthesis pathway. In previous studies, FR-900098 was shown to possess potent antimalarial activity in vitro and in a murine malaria model. In order to provide a basis for further preclinical and clinical development, we studied the acute toxicity and genotoxicity of FR-900098. We observed no acute toxicity in rats, i.e. there were no clinical signs of toxicity and no substance-related deaths after the administration of a single dose of 3000 mg/kg body weight orally or 400 mg/kg body weight intravenously. No mutagenic potential was detected in the Salmonella typhimurium reverse mutation assay (Ames test) or an in vitro mammalian cell gene mutation test using mouse lymphoma L5178Y/TK(+/-) cells (clone 3.7.2C), both with and without metabolic activation. In addition, FR-900098 demonstrated no clastogenic or aneugenic capability or significant adverse effects on blood formation in an in vivo micronucleus test with bone marrow erythrocytes from NMRI mice. We conclude that FR-900098 lacks acute toxicity and genotoxicity, supporting its further development as an antimalarial drug.
Keywords: Ames test; FR-900098; Plasmodium falciparum; acute toxicity; drug development; fosmidomycin; genotoxicity; malaria; micronucleus test; mouse lymphoma assay.
Figures
References
-
- Wiesner J, Reichenberg A, Heinrich S, Schlitzer M, Jomaa H. The plastid-like organelle of apicomplexan parasites as drug target. Curr Pharm Des 2008; 14:855-71; PMID:18473835; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.2174/138161208784041105 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kuzuyama T, Shizimu T, Takahashi S, Seto H. Fosmidomycin, a specific inhibitor of 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase in the nonmevalonate pathway of isoprenoidbiosynthesis. Tetrahedron Lett 1998; 39:7913-6; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/S0040-4039(98)01755-9 - DOI
-
- Zeidler J, Schwender J, Müller C, Wiesner J, Weidemeyer C, Beck E, Jomaa H, Lichtenthaler HK. Inhibition of the non-mevalonate 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate pathway of plant isoprenoid biosynthesis by fosmidomycin. Z Naturforsch C 1998; 53:980-6
-
- Jomaa H, Wiesner J, Sanderbrand S, Altincicek B, Weidemeyer C, Hintz M, Türbachova I, Eberl E, Zeidler J, Lichtenthaler HK, Soldati D, Beck E. Inhibitors of the nonmevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis as antimalarial drugs. Science 1999; 285:1573-6; PMID:10477522; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1126/science.285.5433.1573 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tahar R, Basco LK. 2007. Molecular epidemiology of malaria in Cameroon. XXV. In vitro activity of fosmidomycin and its derivatives against fresh clinical isolates of Plasmodium falciparum and sequence analysis of 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2007; 77:214-20; PMID:17690389 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources