A balanced translocation disrupting BCL2L10 and PNLDC1 segregates with affective psychosis
- PMID: 27260655
- PMCID: PMC5363242
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32465
A balanced translocation disrupting BCL2L10 and PNLDC1 segregates with affective psychosis
Abstract
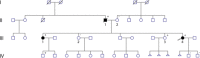
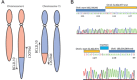
Affective psychoses are a group of severe psychiatric disorders, including schizoaffective disorder and bipolar I disorder, together affecting ∼1% of the population. Despite their high heritability, the molecular genetics and neurobiology of affective psychosis remain largely elusive. Here, we describe the identification of a structural genetic variant segregating with affective psychosis in a family with multiple members suffering from bipolar I disorder or schizoaffective disorder, bipolar type. A balanced translocation involving chromosomes 6 and 15 was detected by karyotyping and fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH). Using whole-genome sequencing, we rapidly delineated the translocation breakpoints as corresponding intragenic events disrupting BCL2L10 and PNLDC1. These data warrant further consideration for BCL2L10 and PNLDC1 as novel candidates for affective psychosis. © 2016 The Authors. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: BCL2L10; PNLDC1; affective psychosis; balanced translocation; bipolar disorder; cytogenetics; schizoaffective disorder; whole-genome sequencing.
© 2016 The Authors. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The serotonin transporter gene 5-HTTLPR polymorphism is associated with affective psychoses but not with schizophrenia: A large-scale study in the Russian population.J Affect Disord. 2017 Jan 15;208:604-609. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.10.020. Epub 2016 Oct 26. J Affect Disord. 2017. PMID: 28029428
-
Chromosome 18 translocation (18;21) (p11.1;p11.1) associated with psychosis in one family.Am J Med Genet. 1996 Nov 22;67(6):560-3. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19961122)67:6<560::AID-AJMG9>3.0.CO;2-L. Am J Med Genet. 1996. PMID: 8950415
-
A balanced chromosomal translocation partially co-segregating with psychotic illness in a family.Psychiatry Res. 1990 Apr;32(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/0165-1781(90)90129-s. Psychiatry Res. 1990. PMID: 2349309
-
Clinical and molecular genetics of psychotic depression.Schizophr Bull. 2013 Jul;39(4):766-75. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbt040. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Schizophr Bull. 2013. PMID: 23512949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An overview of the genetics of psychotic mood disorders.J Psychiatr Res. 2004 Jan;38(1):3-15. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3956(03)00096-7. J Psychiatr Res. 2004. PMID: 14690766 Review.
Cited by
-
Bcl-B: an "unknown" protein of the Bcl-2 family.Biol Direct. 2023 Oct 30;18(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s13062-023-00431-4. Biol Direct. 2023. PMID: 37899453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Variant PNLDC1, Defective piRNA Processing, and Azoospermia.N Engl J Med. 2021 Aug 19;385(8):707-719. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2028973. Epub 2021 Aug 4. N Engl J Med. 2021. PMID: 34347949 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic and neuroimaging approaches to bipolar disorder.BJPsych Open. 2022 Feb 1;8(2):e36. doi: 10.1192/bjo.2021.1082. BJPsych Open. 2022. PMID: 35101157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rediscovering the value of families for psychiatric genetics research.Mol Psychiatry. 2019 Apr;24(4):523-535. doi: 10.1038/s41380-018-0073-x. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Mol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 29955165 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baron M. 2002. Manic‐depression genes and the new millennium: Poised for discovery. Mol Psychiatry 7:342–358. - PubMed
-
- Clements C, Morriss R, Jones S, Peters S, Roberts C, Kapur N. 2013. Suicide in bipolar disorder in a national English sample, 1996–2009: Frequency, trends and characteristics. Psychol Med 43:2593–2602. - PubMed
-
- Cory S, Adams JM. 2002. The Bcl2 family: Regulators of the cellular life‐or‐death switch. Nat Rev Cancer 2:647–656. - PubMed
-
- Drmanac R, Sparks AB, Callow MJ, Halpern AL, Burns NL, Kermani BG, Carnevali P, Nazarenko I, Nilsen GB, Yeung G, Dahl F, Fernandez A, Staker B, Pant KP, Baccash J, Borcherding AP, Brownley A, Cedeno R, Chen L, Chernikoff D, Cheung A, Chirita R, Curson B, Ebert JC, Hacker CR, Hartlage R, Hauser B, Huang S, Jiang Y, Karpinchyk V, Koenig M, Kong C, Landers T, Le C, Liu J, McBride CE, Morenzoni M, Morey RE, Mutch K, Perazich H, Perry K, Peters BA, Peterson J, Pethiyagoda CL, Pothuraju K, Richter C, Rosenbaum AM, Roy S, Shafto J, Sharanhovich U, Shannon KW, Sheppy CG, Sun M, Thakuria JV, Tran A, Vu D, Zaranek AW, Wu X, Drmanac S, Oliphant AR, Banyai WC, Martin B, Ballinger DG, Church GM, Reid CA. 2010. Human genome sequencing using unchained base reads on self‐assembling DNA nanoarrays. Science 327:78–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

