Comprehensive and Holistic Analysis of HT-29 Colorectal Cancer Cells and Tumor-Bearing Nude Mouse Model: Interactions Among Fractions Derived From the Chinese Medicine Formula Tian Xian Liquid in Effects on Human Colorectal Carcinoma
- PMID: 27261455
- PMCID: PMC5759938
- DOI: 10.1177/1534735416651969
Comprehensive and Holistic Analysis of HT-29 Colorectal Cancer Cells and Tumor-Bearing Nude Mouse Model: Interactions Among Fractions Derived From the Chinese Medicine Formula Tian Xian Liquid in Effects on Human Colorectal Carcinoma
Abstract
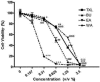
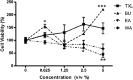
The Chinese medicine formula Tian Xian Liquid (TXL) has been used clinically for cancer therapy in China for more than 25 years. However, the comprehensive and holistic effects of its bioactive fractions for various antitumor therapeutic effects have not been unraveled. This is the first study to scientifically elucidate the holistic effect of Chinese medicine formula for treating colon cancer, hence allowing a better understanding of the essence of Chinese medicine formula, through the comparison of the actions of TXL and its functional constituent fractions, including ethyl acetate (EA), butanol (BU), and aqueous (WA) fractions. Tissue-specific proliferative/antiproliferative effects of these fractions on human colorectal carcinoma HT-29 cells and splenocytes were studied by using the MTT assay. Their modulations on the expression of markers of antiproliferation, antimetastasis, reversion of multidrug resistance in treated HT-29 cells were examined with real-time polymerase chain reaction and Western blot analysis, and their modulations in a xenografted nude mouse model were examined by Western blot analysis. Results revealed that EA fraction slightly inhibited the proliferation of HT-29 cells, but tissue-specifically exerted the most potent antiproliferative effect on splenocytes. On the contrary, only TXL and BU fraction tissue-specifically contributed to the proliferation of splenocytes, but inhibited the proliferation of HT-29 cells. WA fraction exerted the most potent antiproliferative effect on HT-29 cells and also the strongest inhibitory action on tumor size in the nude mouse model in our previous study. In the HT-29 model, TXL and WA fraction exerted the most pronounced effect on upregulation of p21 mRNA and protein; TXL, and EA and WA fractions exerted the effect on downregulation of G1 phase cell cycle protein, cyclin D1 mRNA and protein; EA and BU fractions exerted the most prominent anti-invasive effect on anti-invasion via downregulation of MMP-1 mRNA; TXL potently reversed most multidrug resistance via downregulation of MDR-1 protein. In conclusion, the comprehensive and holistic effects of TXL were demonstrated with ( a) mutual accentuation and mutual enhancement, ( b) mutual counteraction and mutual suppression, and ( c) mutual antagonism among the 3 constituent fractions. Moreover, the design of the present study may lead to further development of more tissue-specific effective drugs with minimal side effects for clinical use in combating carcinoma.
Keywords: Chinese medicinal formula; Tian Xian Liquid; antitumorigenicity; colon cancer; constituent fractions; holistic.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


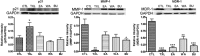
References
-
- American Cancer Society. Global Cancer Facts & Figures. 2nd ed. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society; 2011. http://www.cancer.org/acs/groups/content/@epidemiologysurveilance/docume.... Accessed May 10, 2016.
-
- Pfizer Inc. Pfizer Facts: The Burden of Cancer in Asia. New York, NY: Pfizer Inc; 2008. http://www.pfizer.com/files/products/cancer_in_asia.pdf. Accessed May 10, 2016.
-
- TCM Forum, Hong Kong. Treatment and Aftercare for Colon Cancer in TCM. http://www.tcmforum.com/forum2.php?reply=0&forumID=100404&fgroup=expert. Accessed April 6, 2011.
-
- Cancer Fund, Hong Kong. Latest Cancer Statistics. http://www.cancer-fund.org/en/cancer-statistics.html. Accessed June 27, 2014.
-
- National Cancer Centre, Singapore. Cancer Statistics. http://www.nccs.com.sg/patientcare/whatiscancer/cancerStatistics/Pages/H.... Accessed May 15, 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

