Biology and clinical application of CAR T cells for B cell malignancies
- PMID: 27262700
- PMCID: PMC5512169
- DOI: 10.1007/s12185-016-2039-6
Biology and clinical application of CAR T cells for B cell malignancies
Abstract
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-modified T cells have generated broad interest in oncology following a series of dramatic clinical successes in patients with chemorefractory B cell malignancies. CAR therapy now appears to be on the cusp of regulatory approval as a cell-based immunotherapy. We review here the T cell biology and cell engineering research that led to the development of second generation CARs, the selection of CD19 as a CAR target, and the preclinical studies in animal models that laid the foundation for clinical trials targeting CD19+ malignancies. We further summarize the status of CD19 CAR clinical therapy for non-Hodgkin lymphoma and B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, including their efficacy, toxicities (cytokine release syndrome, neurotoxicity and B cell aplasia) and current management in humans. We conclude with an overview of recent pre-clinical advances in CAR design that argues favorably for the advancement of CAR therapy to tackle other hematological malignancies as well as solid tumors.
Keywords: Adoptive T cell therapy; CD19; Chimeric antigen receptor; Immunotherapy; T cell engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
MLD has no relevant conflict of interests to disclose. MS is a consultant for Juno Therapeutics.
Figures
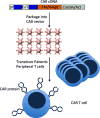
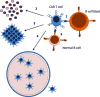
References
-
- Williams MA, Bevan MJ. Effector and memory CTL differentiation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:171–92. - PubMed
-
- Abraham RT, Weiss A. Jurkat T cells and development of the T-cell receptor signalling paradigm. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004 Apr;4(4):301–8. - PubMed
-
- Irving BA, Weiss A. The cytoplasmic domain of the T cell receptor zeta chain is sufficient to couple to receptor-associated signal transduction pathways. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):891–901. - PubMed
-
- Coulie PG, Uyttenhove C, Wauters P, Manolios N, Klausner RD, Samelson LE, et al. Identification of a murine monoclonal antibody specific for an allotypic determinant on mouse CD3. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jul;21(7):1703–9. - PubMed
-
- Letourneur F, Klausner RD. Activation of T cells by a tyrosine kinase activation domain in the cytoplasmic tail of CD3 epsilon. Science. 1992 Jan 3;255(5040):79–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

