Fifty years later: Emerging functions of IgE antibodies in host defense, immune regulation, and allergic diseases
- PMID: 27263999
- PMCID: PMC4898788
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.04.009
Fifty years later: Emerging functions of IgE antibodies in host defense, immune regulation, and allergic diseases
Abstract
Fifty years ago, after a long search, IgE emerged as the circulating factor responsible for triggering allergic reactions. Its extremely low concentration in plasma created significant hurdles for scientists working to reveal its identity. We now know that IgE levels are invariably increased in patients affected by atopic conditions and that IgE provides the critical link between the antigen recognition role of the adaptive immune system and the effector functions of mast cells and basophils at mucosal and cutaneous sites of environmental exposure. This review discusses the established mechanisms of action of IgE in pathologic immediate hypersensitivity, as well as its multifaceted roles in protective immunity, control of mast cell homeostasis, and its more recently revealed immunomodulatory functions.
Keywords: IgE; anaphylaxis; mast cells.
Copyright © 2016 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of potential conflict of interest: H. C. Oettgen has received a grant from the National Institutes of Health and has had consultant arrangements with Genentech.
Figures

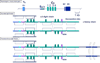
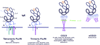
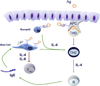
References
-
- Chaudhuri J, Alt FW. Class-switch recombination: interplay of transcription, DNA deamination and DNA repair. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:541–552. - PubMed
-
- Tong P, Wesemann DR. Molecular mechanisms of IgE class switch recombination. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;388:21–37. - PubMed
-
- Cheng G, Cleary AM, Ye Z, Hong DI, Lederman S, Baltimore D. Involvement of CRAF1, a relative of TRAF, in CD40 signaling. Science. 1995;267:1494–1498. - PubMed
-
- Ishida T, Mizushima S, Azuma S, Kobayashi N, Tojo T, Suzuki K, et al. Identification of TRAF6, a novel tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated protein that mediates signaling from an amino-terminal domain of the CD40 cytoplasmic region. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:28745–28748. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

