The role of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons in fear and extinction memory
- PMID: 27264248
- PMCID: PMC4987180
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2016.06.001
The role of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons in fear and extinction memory
Abstract
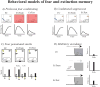
Cholinergic input to the neocortex, dorsal hippocampus (dHipp), and basolateral amygdala (BLA) is critical for neural function and synaptic plasticity in these brain regions. Synaptic plasticity in the neocortex, dHipp, ventral Hipp (vHipp), and BLA has also been implicated in fear and extinction memory. This finding raises the possibility that basal forebrain (BF) cholinergic neurons, the predominant source of acetylcholine in these brain regions, have an important role in mediating fear and extinction memory. While empirical studies support this hypothesis, there are interesting inconsistencies among these studies that raise questions about how best to define the role of BF cholinergic neurons in fear and extinction memory. Nucleus basalis magnocellularis (NBM) cholinergic neurons that project to the BLA are critical for fear memory and contextual fear extinction memory. NBM cholinergic neurons that project to the neocortex are critical for cued and contextual fear conditioned suppression, but are not critical for fear memory in other behavioral paradigms and in the inhibitory avoidance paradigm may even inhibit contextual fear memory formation. Medial septum and diagonal band of Broca cholinergic neurons are critical for contextual fear memory and acquisition of cued fear extinction. Thus, even though the results of previous studies suggest BF cholinergic neurons modulate fear and extinction memory, inconsistent findings among these studies necessitates more research to better define the neural circuits and molecular processes through which BF cholinergic neurons modulate fear and extinction memory. Furthermore, studies determining if BF cholinergic neurons can be manipulated in such a manner so as to treat excessive fear in anxiety disorders are needed.
Keywords: Contextual conditioning; Extinction recall; Fear conditioning; Fear extinction; Inhibitory avoidance; Magnocellular; Nucleus basalis.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cholinergic neuronal lesions in the medial septum and vertical limb of the diagonal bands of Broca induce contextual fear memory generalization and impair acquisition of fear extinction.Hippocampus. 2016 Jun;26(6):718-26. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22553. Epub 2015 Dec 25. Hippocampus. 2016. PMID: 26606423 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of medial septum and diagonal bands of Broca cholinergic projections to the ventral hippocampus disrupt auditory fear memory.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018 Jul;152:71-79. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2018.05.009. Epub 2018 May 18. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018. PMID: 29783059 Free PMC article.
-
Basal forebrain cholinergic signaling in the basolateral amygdala promotes strength and durability of fear memories.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2023 Mar;48(4):605-614. doi: 10.1038/s41386-022-01427-w. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 36056107 Free PMC article.
-
Basal forebrain cholinergic systems as circuits through which traumatic stress disrupts emotional memory regulation.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2024 Apr;159:105569. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2024.105569. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2024. PMID: 38309497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the basolateral amygdala and infralimbic cortex in (re)learning extinction.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Jan;236(1):303-312. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-4957-x. Epub 2018 Jun 30. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 29959461 Review.
Cited by
-
Infralimbic Projections to the Substantia Innominata-Ventral Pallidum Constrain Defensive Behavior during Extinction Learning.J Neurosci. 2025 May 28;45(22):e1001242025. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1001-24.2025. J Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40262898
-
Histamine H1 receptors in dentate gyrus-projecting cholinergic neurons of the medial septum suppress contextual fear retrieval in mice.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 10;15(1):5805. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50042-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38987240 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Mongolian gerbil emotional behavior: effects of two shock intensities and response-independent shocks during an extended inhibitory-avoidance task.PeerJ. 2017 Nov 13;5:e4009. doi: 10.7717/peerj.4009. eCollection 2017. PeerJ. 2017. PMID: 29152417 Free PMC article.
-
Functionally linked amygdala and prefrontal cortical regions are innervated by both single and double projecting cholinergic neurons.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Jul 10;18:1426153. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1426153. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39049824 Free PMC article.
-
Functionally refined encoding of threat memory by distinct populations of basal forebrain cholinergic projection neurons.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 9:rs.3.rs-3938016. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3938016/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2024 Feb 16;13:e86581. doi: 10.7554/eLife.86581. PMID: 38405824 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Abe T, Sugihara H, Nawa H, Shigemoto R, Mizuno N, Nakanishi S. Molecular characterization of a novel metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5 coupled to inositol phosphate/Ca2+ signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:13361–13368. - PubMed
-
- Ashe JH, McKenna TM, Weinberger NM. Cholinergic modulation of frequency receptive fields in auditory cortex: II. Frequency-specific effects of anticholinesterases provide evidence for a modulatory action of endogenous ACh. Synapse. 1989;4:44–54. - PubMed
-
- Baxter MG, Chiba AA. Cognitive functions of the basal forebrain. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1999;9:178–183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

