AMPA Receptor Plasticity in Accumbens Core Contributes to Incubation of Methamphetamine Craving
- PMID: 27264310
- PMCID: PMC5050076
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.04.003
AMPA Receptor Plasticity in Accumbens Core Contributes to Incubation of Methamphetamine Craving
Abstract
Background: The incubation of cue-induced drug craving in rodents provides a model of persistent vulnerability to craving and relapse in human addicts. After prolonged withdrawal, incubated cocaine craving depends on strengthening of nucleus accumbens (NAc) core synapses through incorporation of Ca2+-permeable alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid receptors (CP-AMPARs). Through metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 (mGluR1)-mediated synaptic depression, mGluR1 positive allosteric modulators remove CP-AMPARs from these synapses and thereby reduce cocaine craving. This study aimed to determine if similar plasticity accompanies incubation of methamphetamine craving.
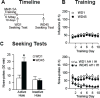
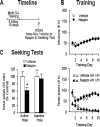
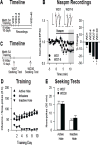
Methods: Rats self-administered saline or methamphetamine under extended-access conditions. Cue-induced seeking tests demonstrated incubation of methamphetamine craving. After withdrawal periods ranging from 1 to >40 days, rats underwent one of the following procedures: 1) whole-cell patch clamp recordings to characterize AMPAR transmission, 2) intra-NAc core injection of the CP-AMPAR antagonist 1-naphthyl acetyl spermine followed by a seeking test, or 3) systemic administration of a mGluR1 positive allosteric modulator followed by a seeking test.
Results: Incubation of methamphetamine craving was associated with CP-AMPAR accumulation in NAc core, and both effects were maximal after ~1 week of withdrawal. Expression of incubated craving was decreased by intra-NAc core 1-naphthyl acetyl spermine injection or systemic mGluR1 positive allosteric modulator administration.
Conclusions: These results are the first to demonstrate a role for the NAc in the incubation of methamphetamine craving and describe adaptations in synaptic transmission associated with this model. They establish that incubation of craving and associated CP-AMPAR plasticity occur much more rapidly during withdrawal from methamphetamine compared with cocaine. However, a common mGluR1-based therapeutic strategy may be helpful for recovering cocaine and methamphetamine addicts.
Keywords: Ca(2+)-permeable AMPA receptors; Extended-access drug self-administration; Incubation of craving; Metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 (mGluR1); Methamphetamine; Nucleus accumbens.
Copyright © 2016 Society of Biological Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial disclosures: The authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
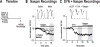

Comment in
-
Synaptic Plasticity: The Role of Learning and Unlearning in Addiction and Beyond.Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Nov 1;80(9):e73-e75. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Biol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27697156 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
AMPA receptor and metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 adaptations in the nucleus accumbens core during incubation of methamphetamine craving.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019 Aug;44(9):1534-1541. doi: 10.1038/s41386-019-0425-5. Epub 2019 May 30. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019. PMID: 31146278 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic depression via mGluR1 positive allosteric modulation suppresses cue-induced cocaine craving.Nat Neurosci. 2014 Jan;17(1):73-80. doi: 10.1038/nn.3590. Epub 2013 Nov 24. Nat Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24270186 Free PMC article.
-
GluA2-lacking AMPA receptors in the nucleus accumbens core and shell contribute to the incubation of oxycodone craving in male rats.Addict Biol. 2022 Nov;27(6):e13237. doi: 10.1111/adb.13237. Addict Biol. 2022. PMID: 36301206 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptations in AMPA receptor transmission in the nucleus accumbens contributing to incubation of cocaine craving.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt B(0 0):287-300. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.061. Epub 2013 May 30. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23727437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using metabotropic glutamate receptors to modulate cocaine's synaptic and behavioral effects: mGluR1 finds a niche.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013 Aug;23(4):500-6. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2013.01.009. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23385114 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synaptic Plasticity: The Role of Learning and Unlearning in Addiction and Beyond.Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Nov 1;80(9):e73-e75. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Biol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27697156 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Drug addiction: from bench to bedside.Transl Psychiatry. 2021 Aug 12;11(1):424. doi: 10.1038/s41398-021-01542-0. Transl Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34385417 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roflumilast treatment during forced abstinence reduces relapse to methamphetamine seeking and taking.Addict Biol. 2022 Jan;27(1):e13082. doi: 10.1111/adb.13082. Epub 2021 Aug 7. Addict Biol. 2022. PMID: 34363284 Free PMC article.
-
Trafficking of calcium-permeable and calcium-impermeable AMPA receptors in nucleus accumbens medium spiny neurons co-cultured with prefrontal cortex neurons.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Apr;116:224-232. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.12.014. Epub 2016 Dec 16. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 27993521 Free PMC article.
-
Updates on the Physiopathology of Group I Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors (mGluRI)-Dependent Long-Term Depression.Cells. 2023 Jun 8;12(12):1588. doi: 10.3390/cells12121588. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37371058 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baicy K, London ED. Corticolimbic dysregulation and chronic methamphetamine abuse. Addiction. 2007;102(Suppl 1):5–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

