DNA polymerase θ (POLQ), double-strand break repair, and cancer
- PMID: 27264557
- PMCID: PMC5114520
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2016.05.003
DNA polymerase θ (POLQ), double-strand break repair, and cancer
Abstract
DNA polymerase theta (pol θ) is encoded in the genomes of many eukaryotes, though not in fungi. Pol θ is encoded by the POLQ gene in mammalian cells. The C-terminal third of the protein is a family A DNA polymerase with additional insertion elements relative to prokaryotic homologs. The N-terminal third is a helicase-like domain with DNA-dependent ATPase activity. Pol θ is important in the repair of genomic double-strand breaks (DSBs) from many sources. These include breaks formed by ionizing radiation and topoisomerase inhibitors, breaks arising at stalled DNA replication forks, breaks introduced during diversification steps of the mammalian immune system, and DSB induced by CRISPR-Cas9. Pol θ participates in a route of DSB repair termed "alternative end-joining" (altEJ). AltEJ is independent of the DNA binding Ku protein complex and requires DNA end resection. Pol θ is able to mediate joining of two resected 3' ends harboring DNA sequence microhomology. "Signatures" of Pol θ action during altEJ are the frequent utilization of longer microhomologies, and the insertion of additional sequences at joining sites. The mechanism of end-joining employs the ability of Pol θ to tightly grasp a 3' terminus through unique contacts in the active site, allowing extension from minimally paired primers. Pol θ is involved in controlling the frequency of chromosome translocations and preserves genome integrity by limiting large deletions. It may also play a backup role in DNA base excision repair. POLQ is a member of a cluster of similarly upregulated genes that are strongly correlated with poor clinical outcome for breast cancer, ovarian cancer and other cancer types. Inhibition of pol θ is a compelling approach for combination therapy of radiosensitization.
Keywords: Alternative end-joining; DNA double strand breaks; DNA polymerase; DNA synthesis; MMEJ; Synthetic lethality.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Statement The authors declare that they have no financial, personal or professional competing interests that could be construed to have influenced this paper.
Figures


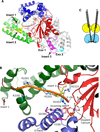
References
-
- Hübscher U, Maga G, Spadari S. Eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 2002;71:133–163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

