Taz1-Shelterin Promotes Facultative Heterochromatin Assembly at Chromosome-Internal Sites Containing Late Replication Origins
- PMID: 27264871
- PMCID: PMC6699828
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.04.034
Taz1-Shelterin Promotes Facultative Heterochromatin Assembly at Chromosome-Internal Sites Containing Late Replication Origins
Abstract
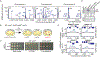
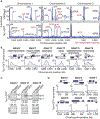
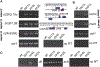
Facultative heterochromatin regulates gene expression, but its assembly is poorly understood. Previously, we identified facultative heterochromatin islands in the fission yeast genome and found that RNA elimination machinery promotes island assembly at meiotic genes. Here, we report that Taz1, a component of the telomere protection complex Shelterin, is required to assemble heterochromatin islands at regions corresponding to late replication origins that are sites of double-strand break formation during meiosis. The loss of Taz1 or other Shelterin subunits, including Ccq1 that interacts with Clr4/Suv39h, abolishes heterochromatin at late origins and causes derepression of associated genes. Moreover, the late-origin regulator Rif1 affects heterochromatin at Taz1-dependent islands and subtelomeric regions. We explore the connection between facultative heterochromatin and replication control and show that heterochromatin machinery affects replication timing. These analyses reveal the role of Shelterin in facultative heterochromatin assembly at late origins, which has important implications for genome stability and gene regulation.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
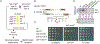

References
-
- Aladjem MI (2007). Replication in context: dynamic regulation of DNA replication patterns in metazoans. Nat. Rev. Genet 8, 588–600. - PubMed
-
- Bahler J, Wu JQ, Longtine MS, Shah NG, McKenzie A 3rd, Steever AB, Wach A, Philippsen P, and Pringle JR (1998). Heterologous modules for efficient and versatile PCR-based gene targeting in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Yeast 14, 943–951. - PubMed
-
- Baumann P, and Cech TR (2001). Pot1, the putative telomere end-binding protein in fission yeast and humans. Science 292, 1171–1175. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

