A carnosine intervention study in overweight human volunteers: bioavailability and reactive carbonyl species sequestering effect
- PMID: 27265207
- PMCID: PMC4893669
- DOI: 10.1038/srep27224
A carnosine intervention study in overweight human volunteers: bioavailability and reactive carbonyl species sequestering effect
Abstract
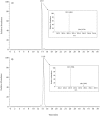
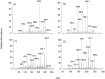
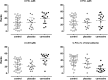
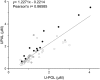
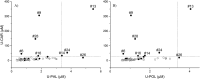
Carnosine is a natural dipeptide able to react with reactive carbonyl species, which have been recently associated with the onset and progression of several human diseases. Herein, we report an intervention study in overweight individuals. Carnosine (2 g/day) was orally administered for twelve weeks in order to evaluate its bioavailability and metabolic fate. Two carnosine adducts were detected in the urine samples of all subjects. Such adducts are generated from a reaction with acrolein, which is one of the most toxic and reactive compounds among reactive carbonyl species. However, neither carnosine nor adducts have been detected in plasma. Urinary excretion of adducts and carnosine showed a positive correlation although a high variability of individual response to carnosine supplementation was observed. Interestingly, treated subjects showed a significant decrease in the percentage of excreted adducts in reduced form, accompanied by a significant increase of the urinary excretion of both carnosine and carnosine-acrolein adducts. Altogether, data suggest that acrolein is entrapped in vivo by carnosine although the response to its supplementation is possibly influenced by individual diversities in terms of carnosine dietary intake, metabolism and basal production of reactive carbonyl species.
Figures

References
-
- Semchyshyn H. M. & Lushchak V. I. Oxidative Stress-Molecular Mechanisms and Biological Effects (ed Lushchak Dr. Volodymyr) Ch. 2, 15–46 (InTech, 2012).
-
- Aldini G. et al.. Lipoxidation-derived reactive carbonyl species as potential drug targets in preventing protein carbonylation and related cellular dysfunction. ChemMedChem 1, 1045-+ (2006). - PubMed
-
- Dalle-Donne I., Giustarini D., Colombo R., Rossi R. & Milzani A. Protein carbonylation in human diseases. Trends Mol Med 9, 169–176 (2003). - PubMed
-
- O’Brien P. J., Siraki A. G. & Shangari N. Aldehyde sources, metabolism, molecular toxicity mechanisms, and possible effects on human health. Crit Rev Toxicol 35, 609–662 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

