Accurate prediction of RNA-binding protein residues with two discriminative structural descriptors
- PMID: 27266516
- PMCID: PMC4897909
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-016-1110-x
Accurate prediction of RNA-binding protein residues with two discriminative structural descriptors
Abstract
Background: RNA-binding proteins participate in many important biological processes concerning RNA-mediated gene regulation, and several computational methods have been recently developed to predict the protein-RNA interactions of RNA-binding proteins. Newly developed discriminative descriptors will help to improve the prediction accuracy of these prediction methods and provide further meaningful information for researchers.
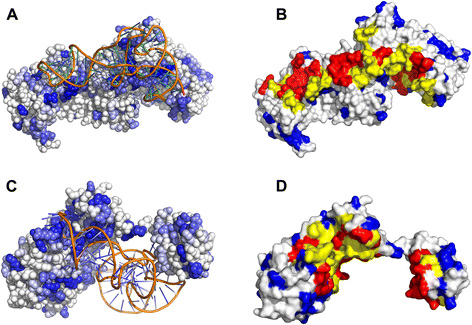
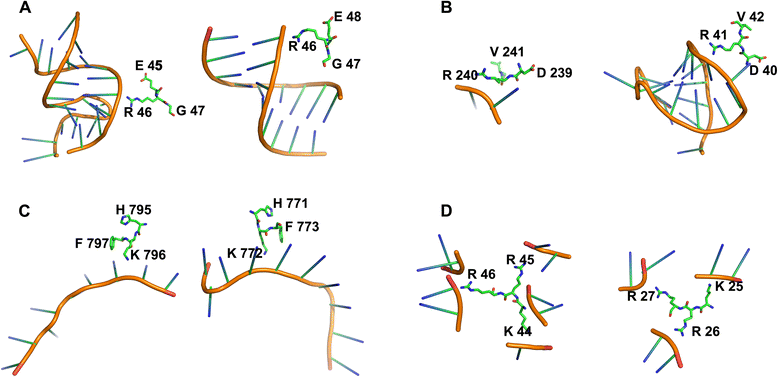
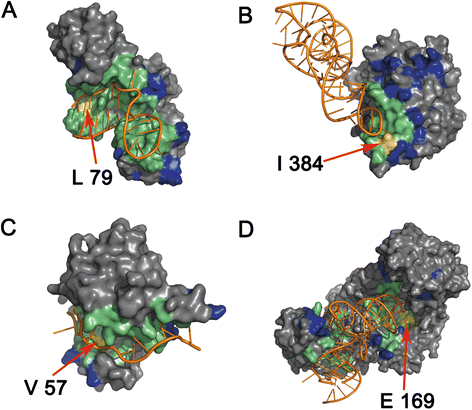
Results: In this work, we designed two structural features (residue electrostatic surface potential and triplet interface propensity) and according to the statistical and structural analysis of protein-RNA complexes, the two features were powerful for identifying RNA-binding protein residues. Using these two features and other excellent structure- and sequence-based features, a random forest classifier was constructed to predict RNA-binding residues. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of five-fold cross-validation for our method on training set RBP195 was 0.900, and when applied to the test set RBP68, the prediction accuracy (ACC) was 0.868, and the F-score was 0.631.
Conclusions: The good prediction performance of our method revealed that the two newly designed descriptors could be discriminative for inferring protein residues interacting with RNAs. To facilitate the use of our method, a web-server called RNAProSite, which implements the proposed method, was constructed and is freely available at http://lilab.ecust.edu.cn/NABind .
Keywords: Protein-RNA interactions; Random forest classifier; Residue electrostatic surface potential; Residue triplet interface propensity; Structural analysis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prediction of RNA-binding residues in proteins from primary sequence using an enriched random forest model with a novel hybrid feature.Proteins. 2011 Apr;79(4):1230-9. doi: 10.1002/prot.22958. Epub 2011 Jan 25. Proteins. 2011. PMID: 21268114
-
3dRPC: a web server for 3D RNA-protein structure prediction.Bioinformatics. 2018 Apr 1;34(7):1238-1240. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx742. Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 29186336
-
Prediction of protein-RNA binding sites by a random forest method with combined features.Bioinformatics. 2010 Jul 1;26(13):1616-22. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq253. Epub 2010 May 18. Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20483814
-
Computational Prediction of RNA-Binding Proteins and Binding Sites.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Nov 3;16(11):26303-17. doi: 10.3390/ijms161125952. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26540053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational methods for prediction of protein-RNA interactions.J Struct Biol. 2012 Sep;179(3):261-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2011.10.001. Epub 2011 Oct 12. J Struct Biol. 2012. PMID: 22019768 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent applications of deep learning and machine intelligence on in silico drug discovery: methods, tools and databases.Brief Bioinform. 2019 Sep 27;20(5):1878-1912. doi: 10.1093/bib/bby061. Brief Bioinform. 2019. PMID: 30084866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Individually double minimum-distance definition of protein-RNA binding residues and application to structure-based prediction.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2018 Dec;32(12):1363-1373. doi: 10.1007/s10822-018-0177-z. Epub 2018 Nov 26. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2018. PMID: 30478757
-
A comprehensive review of protein-centric predictors for biomolecular interactions: from proteins to nucleic acids and beyond.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Mar 27;25(3):bbae162. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae162. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 38739759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein-RNA interaction prediction with deep learning: structure matters.Brief Bioinform. 2022 Jan 17;23(1):bbab540. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab540. Brief Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 34929730 Free PMC article.
-
HybridRNAbind: prediction of RNA interacting residues across structure-annotated and disorder-annotated proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Mar 21;51(5):e25. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1253. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36629262 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

