Interleukin-6: an emerging regulator of pathological pain
- PMID: 27267059
- PMCID: PMC4897919
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-016-0607-6
Interleukin-6: an emerging regulator of pathological pain
Abstract
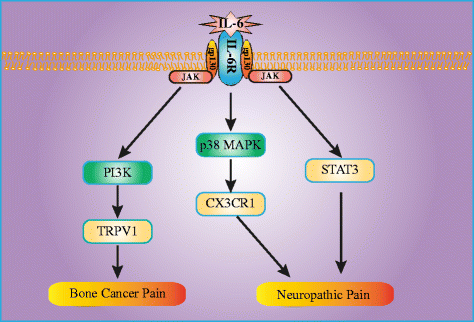
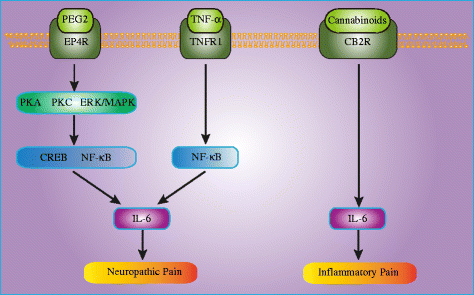
Interleukin-6 is an inflammatory cytokine with wide-ranging biological effects. It has been widely demonstrated that neuroinflammation plays a critical role in the development of pathological pain. Recently, various pathological pain models have shown elevated expression levels of interleukin-6 and its receptor in the spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia. Additionally, the administration of interleukin-6 could cause mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia, and an intrathecal injection of anti-interleukin-6 neutralizing antibody alleviated these pain-related behaviors. These studies indicated a pivotal role of interleukin-6 in pathological pain. In this review, we summarize the recent progress in understanding the roles and mechanisms of interleukin-6 in mediating pathological pain associated with bone cancer, peripheral nerve injury, spinal cord injury, chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, complete Freund's adjuvant injection, and carrageenan injection. Understanding and regulating interleukin-6 could be an interesting lead to novel therapeutic strategies for pathological pain.
Keywords: Bone cancer pain; Inflammatory pain; Interleukin-6; Neuropathic pain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-17 contributes to neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain following peripheral nerve injury in mice.J Pain. 2011 Mar;12(3):370-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2010.08.003. J Pain. 2011. PMID: 20889388
-
The critical role of invading peripheral macrophage-derived interleukin-6 in vincristine-induced mechanical allodynia in mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Sep 11;592(1-3):87-92. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.07.008. Epub 2008 Jul 10. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18652822
-
Aspirin-triggered Lipoxin A4 attenuates mechanical allodynia in association with inhibiting spinal JAK2/STAT3 signaling in neuropathic pain in rats.Neuroscience. 2014 Jul 25;273:65-78. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.04.052. Epub 2014 May 14. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24836854
-
Interleukin-17: A Putative Novel Pharmacological Target for Pathological Pain.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024;22(2):204-216. doi: 10.2174/1570159X21666230811142713. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37581321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of curcumin in the management of pathological pain.Phytomedicine. 2018 Sep 15;48:129-140. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.04.045. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30195871 Review.
Cited by
-
Acute Cytokine Response During Breast Cancer Surgery: Potential Role of Dexamethasone and Lidocaine and Relationship with Postoperative Pain and Complications - Analysis of Three Pooled Pilot Randomized Controlled Trials.J Pain Res. 2020 May 27;13:1243-1254. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S252377. eCollection 2020. J Pain Res. 2020. PMID: 32547185 Free PMC article.
-
The blockade of CC chemokine receptor type 1 influences the level of nociceptive factors and enhances opioid analgesic potency in a rat model of neuropathic pain.Immunology. 2020 Apr;159(4):413-428. doi: 10.1111/imm.13172. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Immunology. 2020. PMID: 31919846 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous-flow cryocompression therapy penetrates to bone level in hip fracture patients in a numerical simulation.J Orthop Surg Res. 2019 Feb 14;14(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s13018-019-1081-5. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019. PMID: 30764844 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved Expression of Nav1.7 and Nav1.8 Contribute to the Spontaneous and Thermally Evoked Excitability in IL-6 and NGF-Sensitized Adult Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons In Vitro.Bioengineering (Basel). 2020 May 16;7(2):44. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering7020044. Bioengineering (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32429423 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of IL-6 signaling prevents paclitaxel-induced neuropathy in C57Bl/6 mice.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jan 22;11(1):45. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2239-0. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 31969555 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Ke C, Gao F, Tian X, Li C, Shi D, He W, Tian Y. Slit2/Robo1 mediation of synaptic plasticity contributes to bone cancer pain. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26738857?dopt=Citation. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

