Chromosome fusions triggered by noncoding RNA
- PMID: 27267579
- PMCID: PMC5449082
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1195940
Chromosome fusions triggered by noncoding RNA
Abstract
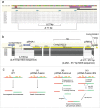
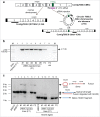
Chromosomal fusions are common in normal and cancer cells and can produce aberrant gene products that promote transformation. The mechanisms driving these fusions are poorly understood, but recurrent fusions are widespread. This suggests an underlying mechanism, and some authors have proposed a possible role for RNA in this process. The unicellular eukaryote Oxytricha trifallax displays an exorbitant capacity for natural genome editing, when it rewrites its germline genome to form a somatic epigenome. This developmental process provides a powerful model system to directly test the influence of small noncoding RNAs on chromosome fusion events during somatic differentiation. Here we show that small RNAs are capable of inducing chromosome fusions in 4 distinct cases (out of 4 tested), including one fusion of 3 chromosomes. We further show that these RNA-mediated chromosome fusions are heritable over multiple sexual generations and that transmission of the acquired fusion is associated with endogenous production of novel piRNA molecules that target the fused junction. We also demonstrate the capacity of a long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) to induce chromosome fusion of 2 distal germline loci. These results underscore the ability of short-lived, aberrant RNAs to act as drivers of chromosome fusion events that can be stably transmitted to future generations.
Keywords: Chromosome fusion; Oxytricha; long noncoding RNA; piRNAs.
Figures



References
-
- Sankar S, Lessnick SL. Promiscuous partnerships in Ewing's sarcoma. Cancer Genet 2011; 204:351-65; PMID:21872822; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cancergen.2011.07.008 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mitelman F, Johansson B, Mertens F. The impact of translocations and gene fusions on cancer causation. Nat Rev Cancer 2007; 7:233-45; PMID:17361217; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrc2091 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Heisterkamp N, Jenster G, Tenhoeve J, Zovich D, Pattengale PK, Groffen J. Acute-Leukemia in Bcr/Abl Transgenic Mice. Nature 1990; 344:251-3; PMID:2179728; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/344251a0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Adams JM, Harris AW, Pinkert CA, Corcoran LM, Alexander WS, Cory S, Palmiter RD, Brinster RL. The C-Myc Oncogene Driven by Immunoglobulin Enhancers Induces Lymphoid Malignancy in Transgenic Mice. Nature 1985; 318:533-8; PMID:3906410; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/318533a0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Daley GQ, Vanetten RA, Baltimore D. Induction of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia in Mice by the P210bcr/Abl Gene of the Philadelphia-Chromosome. Science 1990; 247:824-30; PMID:2406902; http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.2406902 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
