Association between multimorbidity patterns and chronic pain in elderly primary care patients: a cross-sectional observational study
- PMID: 27267905
- PMCID: PMC4895952
- DOI: 10.1186/s12875-016-0468-1
Association between multimorbidity patterns and chronic pain in elderly primary care patients: a cross-sectional observational study
Abstract
Background: Multimorbidity is a highly prevalent health problem, which may reduce adherence, produce conflicts in treatment, and is not yet supported by evidence-based clinical recommendations. Many older people suffer from more than one chronic disease as well as from chronic pain. There is some evidence that disease management can become more complex if multimorbid patients suffer from chronic pain. In order to better consider the patients' comorbidity spectrum in clinical pain treatment recommendations, evidence is needed regarding which disease combinations are frequently related with the presence of chronic pain. Therefore, our aim is to identify diseases and disease combinations in a multimorbid population, which are associated with the patient-reported presence of chronic pain.
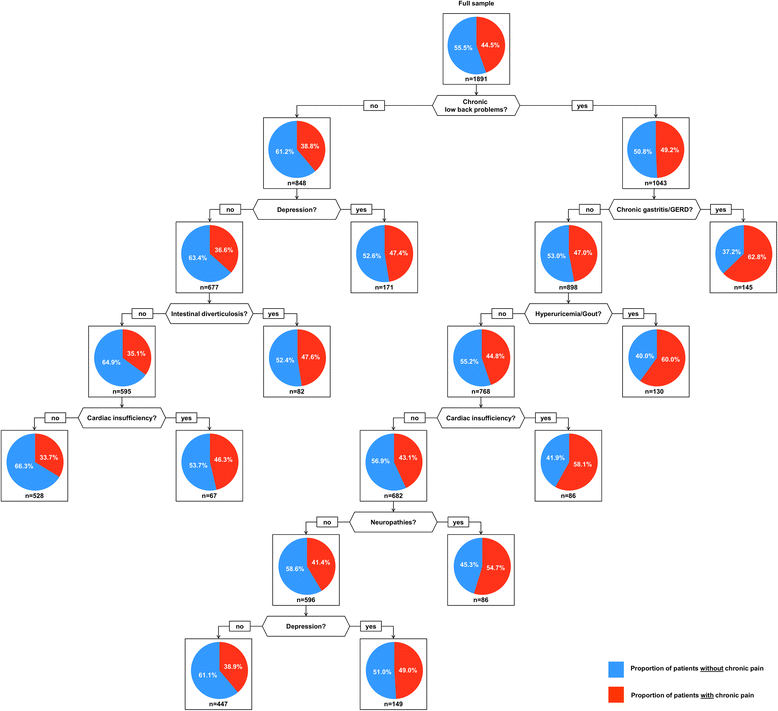
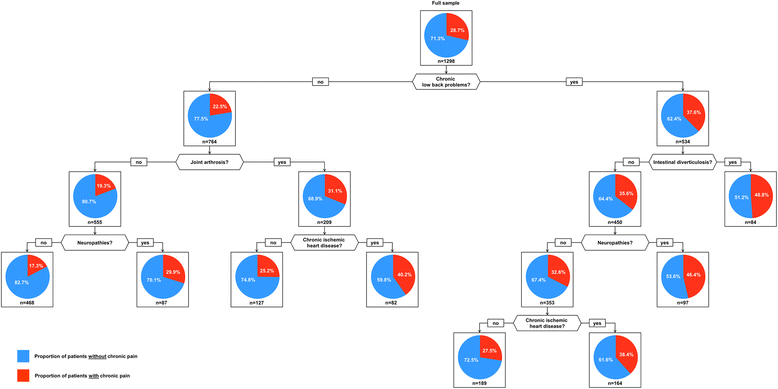
Methods: Analyses are based on cross-sectional data of the MultiCare Cohort Study, an observational cohort study based on interviews with 3189 multimorbid patients aged 65+, randomly selected from 158 practices, and their GPs. The response rate was 46.2 %. Data were collected in GP interviews and comprehensive patient interviews. Diseases and disease combinations associated with chronic pain were identified by CART (classification and regression tree) analyses performed separately for both genders. 46 chronic conditions were used as predictor variables and a dichotomized score from the Graded Chronic Pain Scale was used as outcome variable.
Results: About 60 % of the study participants were female. Women more often reported chronic pain than men. The most important predictor of a higher pain level in the female population was chronic low back problems, especially if combined with chronic gastritis, hyperuricemia/gout, cardiac insufficiency, neuropathies or depression. Regarding the pain level the male population was also divided best by chronic low back problems, especially if combined with intestinal diverticulosis, neuropathies or chronic ischemic heart disease.
Conclusions: Our analyses are a first step in identifying diseases and disease combinations that are related to chronic pain. The most important condition seems to be low back problems. Back pain and pain in other body regions seems to be interrelated with cardiometabolic conditions. In women, psychosocial issues like depression also seem to be relevant.
Trial registration: ISRCTN89818205 .
Keywords: CART analysis; Chronic pain; Epidemiology; Exporative analysis; Low back pain; Multimorbidity; Patient-reported outcomes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The influence of age, gender and socio-economic status on multimorbidity patterns in primary care. First results from the multicare cohort study.BMC Health Serv Res. 2012 Apr 3;12:89. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-12-89. BMC Health Serv Res. 2012. PMID: 22471952 Free PMC article.
-
Multimorbidity patterns in a primary care population aged 55 years and over.Fam Pract. 2015 Oct;32(5):505-13. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmv037. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Fam Pract. 2015. PMID: 26040310 Free PMC article.
-
Which chronic diseases and disease combinations are specific to multimorbidity in the elderly? Results of a claims data based cross-sectional study in Germany.BMC Public Health. 2011 Feb 14;11:101. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-11-101. BMC Public Health. 2011. PMID: 21320345 Free PMC article.
-
Depression and chronic pain in the elderly: links and management challenges.Clin Interv Aging. 2017 Apr 21;12:709-720. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S113576. eCollection 2017. Clin Interv Aging. 2017. PMID: 28461745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Multimorbidity management and the physician's daily clinical dilemma].Internist (Berl). 2017 Apr;58(4):344-353. doi: 10.1007/s00108-017-0200-9. Internist (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28246687 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Making care more patient centered; experiences of healthcare professionals and patients with multimorbidity in the primary care setting.BMC Fam Pract. 2021 Apr 9;22(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s12875-021-01420-0. BMC Fam Pract. 2021. PMID: 33836652 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency and Correlates of Multimorbidity Among the Oldest Old: Study Findings from the Representative "Survey on Quality of Life and Subjective Well-Being of the Very Old in North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW80+)".Clin Interv Aging. 2023 Jan 11;18:41-48. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S388469. eCollection 2023. Clin Interv Aging. 2023. PMID: 36660544 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of multimorbidity in Germany: impact of age and educational level in a cross-sectional study on 19,294 adults.BMC Public Health. 2017 Oct 18;17(1):826. doi: 10.1186/s12889-017-4833-3. BMC Public Health. 2017. PMID: 29047341 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with pain at the end-of-life among older adults in Mexico.Public Health. 2021 Feb;191:68-77. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2020.11.025. Epub 2021 Feb 2. Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33540186 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of chronic pain in LTCs and multimorbidity: A cross-sectional study using UK Biobank.J Multimorb Comorb. 2021 Dec 21;11:26335565211005870. doi: 10.1177/26335565211005870. eCollection 2021 Jan-Dec. J Multimorb Comorb. 2021. PMID: 35004337 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marengoni A, Angleman S, Melis R, Mangialasche F, Karp A, Garmen A, Meinow B, Fratiglioni L. Aging with multimorbidity: a systematic review of the literature. Ageing Res Rev. 2011;10:430–9. - PubMed
-
- Van den Akker M, Buntinx F, Knottnerus JA. Comorbidity or multimorbidity: what’s in a name? A review of literature. Eur J Gen Pract. 1996;2:65–70. doi: 10.3109/13814789609162146. - DOI
-
- Schäfer I, Hansen H, Schön G, Maier W, Höfels S, Altiner A, Fuchs A, Gerlach FM, Petersen JJ, Gensichen J, Schulz S, Riedel-Heller S, Luppa M, Weyerer S, Werle J, Bickel H, Barth K, König HH, Rudolph A, Wiese B, Prokein J, Bullinger M, von dem Knesebeck O, Eisele M, Kaduszkiewicz H, Wegscheider K, van den Bussche H. The German MultiCare-study: patterns of multimorbidity in primary health care - protocol of a prospective cohort study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2009;9:145. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical