Chemical probes of quorum sensing: from compound development to biological discovery
- PMID: 27268906
- PMCID: PMC5007280
- DOI: 10.1093/femsre/fuw009
Chemical probes of quorum sensing: from compound development to biological discovery
Abstract
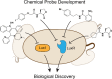
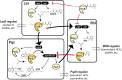
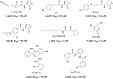
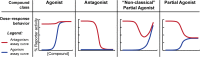
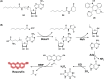
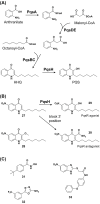
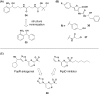
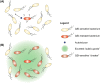
Bacteria can utilize chemical signals to coordinate the expression of group-beneficial behaviors in a method of cell-cell communication called quorum sensing (QS). The discovery that QS controls the production of virulence factors and biofilm formation in many common pathogens has driven an explosion of research aimed at both deepening our fundamental understanding of these regulatory networks and developing chemical agents that can attenuate QS signaling. The inherently chemical nature of QS makes studying these pathways with small molecule tools a complementary approach to traditional microbiology techniques. Indeed, chemical tools are beginning to yield new insights into QS regulation and provide novel strategies to inhibit QS. Here, we review the most recent advances in the development of chemical probes of QS systems in Gram-negative bacteria, with an emphasis on the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa We first describe reports of novel small molecule modulators of QS receptors and QS signal synthases. Next, in several case studies, we showcase how chemical tools have been deployed to reveal new knowledge of QS biology and outline lessons for how researchers might best target QS to combat bacterial virulence. To close, we detail the outstanding challenges in the field and suggest strategies to overcome these issues.
Keywords: LuxR-type receptor; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; acylated homoserine lactone; antivirulence; chemical biology; quorum sensing.
© FEMS 2016. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Analysis of quorum sensing-dependent virulence factor production and its relationship with antimicrobial susceptibility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa respiratory isolates.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010 Dec;16(12):1770-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03177.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010. PMID: 20132256
-
Active efflux influences the potency of quorum sensing inhibitors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Chembiochem. 2014 Feb 10;15(3):435-42. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201300701. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Chembiochem. 2014. PMID: 24478193 Free PMC article.
-
An evolving perspective on the Pseudomonas aeruginosa orphan quorum sensing regulator QscR.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Oct 28;4:152. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00152. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25389523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of natural product inhibitors of quorum sensing reveals competitive inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa RhlR by ortho-vanillin.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Sep 3;12(9):e0068124. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00681-24. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 39046261 Free PMC article.
-
Flexibility and Adaptability of Quorum Sensing in Nature.Trends Microbiol. 2020 Jun;28(6):436-444. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2019.12.004. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Trends Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32001099 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nanotechnology-Based Drug Delivery Systems to Control Bacterial-Biofilm-Associated Lung Infections.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Nov 3;15(11):2582. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15112582. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38004561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modular Synthetic Routes to Fluorine-Containing Halogenated Phenazine and Acridine Agents That Induce Rapid Iron Starvation in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms.ACS Infect Dis. 2022 Feb 11;8(2):280-295. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00402. Epub 2022 Jan 28. ACS Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35089005 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of natural product inhibitors of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa reveals competitive inhibition of RhlR by ortho-vanillin.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 13:2024.02.24.581676. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.24.581676. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Sep 3;12(9):e0068124. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00681-24. PMID: 38559250 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Novel Electrophilic Scaffold for Imaging of Essential Penicillin-Binding Proteins in Streptococcus pneumoniae.ACS Chem Biol. 2017 Nov 17;12(11):2849-2857. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.7b00614. Epub 2017 Oct 18. ACS Chem Biol. 2017. PMID: 28990753 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum Quenching of Nitrobacter winogradskyi Suggests that Quorum Sensing Regulates Fluxes of Nitrogen Oxide(s) during Nitrification.mBio. 2016 Oct 25;7(5):e01753-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01753-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27795404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allegretta G, Weidel E, Empting M, et al. Catechol-based substrates of chalcone synthase as a scaffold for novel inhibitors of PqsD. Eur J Med Chem. 2015;90:351–9. - PubMed
-
- Allen RC, Popat R, Diggle SP, et al. Targeting virulence: can we make evolution-proof drugs? Nat Rev Microbiol. 2014;12:300–8. - PubMed
-
- Amara N, Mashiach R, Amar D, et al. Covalent inhibition of bacterial quorum sensing. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:10610–9. - PubMed
-
- Amara N, Gregor R, Rayo J, et al. Fine-tuning covalent inhibition of bacterial quorum sensing. ChemBioChem. 2016;17:825–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

