Simultaneous optical and electrical in vivo analysis of the enteric nervous system
- PMID: 27270085
- PMCID: PMC4899629
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11800
Simultaneous optical and electrical in vivo analysis of the enteric nervous system
Abstract
The enteric nervous system (ENS) is a major division of the nervous system and vital to the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and its communication with the rest of the body. Unlike the brain and spinal cord, relatively little is known about the ENS in part because of the inability to directly monitor its activity in live animals. Here, we integrate a transparent graphene sensor with a customized abdominal window for simultaneous optical and electrical recording of the ENS in vivo. The implanted device captures ENS responses to neurotransmitters, drugs and optogenetic manipulation in real time.
Figures
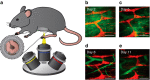
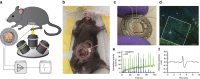

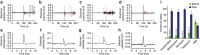
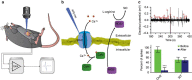
Comment in
-
Neurogastroenterology: A window on the ENS.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Aug;13(8):436-7. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2016.103. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 27329804 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gershon M. D. The enteric nervous system: a second brain. Hosp Pract (1995) 34, 31–32 35-38, 41-32 passim (1999). - PubMed
-
- Campbell I. Gut motility and its control. Anaesth. Intensive Care Med. 13, 59–61 (2012).
-
- Bouche P., Le Forestier N., Maisonobe T., Fournier E. & Willer J. C. Electrophysiological diagnosis of motor neuron disease and pure motor neuropathy. J. Neurol. 246, 520–525 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Jones M. P., Dilley J. B., Drossman D. & Crowell M. D. Brain-gut connections in functional GI disorders: anatomic and physiologic relationships. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 18, 91–103 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

