Relationship of proximal tubular injury to chronic kidney disease as assessed by urinary kidney injury molecule-1 in five cohort studies
- PMID: 27270293
- PMCID: PMC5009290
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfw203
Relationship of proximal tubular injury to chronic kidney disease as assessed by urinary kidney injury molecule-1 in five cohort studies
Abstract
Background: The primary biomarkers used to define CKD are serum creatinine and albuminuria. These biomarkers have directed focus on the filtration and barrier functions of the kidney glomerulus even though albuminuria results from tubule dysfunction as well. Given that proximal tubules make up ∼90% of kidney cortical mass, we evaluated whether a sensitive and specific marker of proximal tubule injury, urinary kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), is elevated in individuals with CKD or with risk factors for CKD.
Methods: We measured urinary KIM-1 in participants of five cohort studies from the USA and Sweden. Participants had a wide range of kidney function and were racially and ethnically diverse. Multivariable linear regression models were used to test the association of urinary KIM-1 with demographic, clinical and laboratory values.
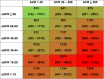
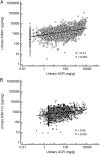
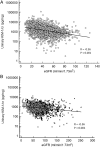
Results: In pooled, multivariable-adjusted analyses, log-transformed, creatinine-normalized urinary KIM-1 levels were higher in those with lower eGFR {β = -0.03 per 10 mL/min/1.73 m(2) [95% confidence interval (CI) -0.05 to -0.02]} and greater albuminuria [β = 0.16 per unit of log albumin:creatinine ratio (95% CI 0.15-0.17)]. Urinary KIM-1 levels were higher in current smokers, lower in blacks than nonblacks and lower in users versus nonusers of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers.
Conclusion: Proximal tubule injury appears to be an integral and measurable element of multiple stages of CKD.
Keywords: KIM-1; albuminuria; chronic kidney disease.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Russo LM, Sandoval RM, McKee M et al. . The normal kidney filters nephrotic levels of albumin retrieved by proximal tubule cells: retrieval is disrupted in nephrotic states. Kidney Int 2007; 71: 504–513 - PubMed
-
- Ichimura T, Bonventre JV, Bailly V et al. . Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), a putative epithelial cell adhesion molecule containing a novel immunoglobulin domain, is up-regulated in renal cells after injury. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 4135–4142 - PubMed
-
- Han WK, Bailly V, Abichandani R et al. . Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1): a novel biomarker for human renal proximal tubule injury. Kidney Int 2002; 62: 237–244 - PubMed
-
- Ichimura T, Hung CC, Yang SA et al. . Kidney injury molecule-1: a tissue and urinary biomarker for nephrotoxicant-induced renal injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2004; 286: F552–F563 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK061028/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000433/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085660/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK093574/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061021/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001878/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM103337/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060980/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060963/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085673/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK039773/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK104308/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085651/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061022/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072381/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000003/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085649/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000424/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016500/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085689/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085688/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029879/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

