Mechanism of Action and Applications of Interleukin 24 in Immunotherapy
- PMID: 27271601
- PMCID: PMC4926403
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17060869
Mechanism of Action and Applications of Interleukin 24 in Immunotherapy
Abstract
Interleukin 24 (IL-24) is an important pleiotropic immunoregulatory cytokine, whose gene is located in human chromosome 1q32-33. IL-24's signaling pathways have diverse biological functions related to cell differentiation, proliferation, development, apoptosis, and inflammation, placing it at the center of an active area of research. IL-24 is well known for its apoptotic effect in cancer cells while having no such effect on normal cells. IL-24 can also be secreted by both immune and non-immune cells. Downstream effects of IL-24, after binding to the IL-20 receptor, can occur dependently or independently of the JAK/STAT signal transduction pathway, which is classically involved in cytokine-mediated activities. After exogenous addition of IL-24, apoptosis is induced in tumor cells independently of the JAK/STAT pathway. We have shown that IL-24 binds to Sigma 1 Receptor and this event induces endoplasmic reticulum stress, calcium mobilization, reactive oxygen species generation, p38MAPK activity, and ceramide production. Here we review IL-24's role in autoimmunity, infectious disease response, wound repair, and vascular disease. Detailed understanding of the pleiotropic roles of IL-24 signaling can assist in the selection of more accurate therapeutic approaches, as well as targeting of appropriate cell types in treatment strategy development, and ultimately achieve desired therapeutic effects.
Keywords: IL-24; Sigma 1 Receptor; cancer; endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress; inflammatory disease.
Figures
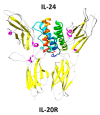
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

