Hand- and Object-Mouthing of Rural Bangladeshi Children 3-18 Months Old
- PMID: 27271651
- PMCID: PMC4924020
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph13060563
Hand- and Object-Mouthing of Rural Bangladeshi Children 3-18 Months Old
Abstract
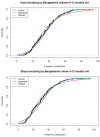
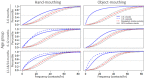
Children are exposed to environmental contaminants by placing contaminated hands or objects in their mouths. We quantified hand- and object-mouthing frequencies of Bangladeshi children and determined if they differ from those of U.S. children to evaluate the appropriateness of applying U.S. exposure models in other socio-cultural contexts. We conducted a five-hour structured observation of the mouthing behaviors of 148 rural Bangladeshi children aged 3-18 months. We modeled mouthing frequencies using 2-parameter Weibull distributions to compare the modeled medians with those of U.S. children. In Bangladesh the median frequency of hand-mouthing was 37.3 contacts/h for children 3-6 months old, 34.4 contacts/h for children 6-12 months old, and 29.7 contacts/h for children 12-18 months old. The median frequency of object-mouthing was 23.1 contacts/h for children 3-6 months old, 29.6 contacts/h for children 6-12 months old, and 15.2 contacts/h for children 12-18 months old. At all ages both hand- and object-mouthing frequencies were higher than those of U.S. children. Mouthing frequencies were not associated with child location (indoor/outdoor). Using hand- and object-mouthing exposure models from U.S. and other high-income countries might not accurately estimate children's exposure to environmental contaminants via mouthing in low- and middle-income countries.
Keywords: Bangladesh; child behavior; exposure factors; mouthing; non-dietary ingestion; rural.
Figures


References
-
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency . Exposure Factors Handbook: 2011 Edition (EPA/600/R-090/052F) U.S. Environmental Protection Agency; Washington, DC, USA: 2011.
-
- Canales R.A., Leckie J.O. Application of a stochastic model to estimate children’s short-term residential exposure to lead. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2007;21:737–745. doi: 10.1007/s00477-006-0086-x. - DOI
-
- Zartarian V.G., Xue J., Özkaynak H., Dang W., Glen G., Smith L., Stallings C. A Probabilistic Arsenic Exposure Assessment for Children Who Contact CCA-Treated Playsets and Decks, Part 1: Model Methodology, Variability Results, Model Evaluation. Risk Anal. 2006;26:515–531. doi: 10.1111/j.1539-6924.2006.00747.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xue J., Zartarian V.G., Özkaynak H., Dang W., Glen G., Smith L., Stallings C. A probabilistic arsenic exposure assessment for children who contact chromated copper arsenate (CCA)-treated playsets and decks, Part 2: Sensitivity and uncertainty analyses. Risk Anal. 2006;26:533–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1539-6924.2006.00748.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

