Analysis of miRNAs and their target genes associated with lipid metabolism in duck liver
- PMID: 27272010
- PMCID: PMC4897641
- DOI: 10.1038/srep27418
Analysis of miRNAs and their target genes associated with lipid metabolism in duck liver
Abstract
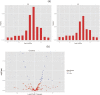
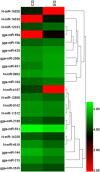
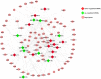
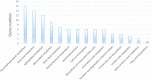
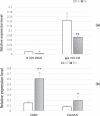
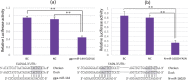
Fat character is an important index in duck culture that linked to local flavor, feed cost and fat intake for costumers. Since the regulation networks in duck lipid metabolism had not been reported very clearly, we aimed to explore the potential miRNA-mRNA pairs and their regulatory roles in duck lipid metabolism. Here, Cherry-Valley ducks were selected and treated with/without 5% oil added in feed for 2 weeks, and then fat content determination was performed on. The data showed that the fat contents and the fatty acid ratios of C17:1 and C18:2 were up-regulated in livers of oil-added ducks, while the C12:0 ratio was down-regulated. Then 21 differential miRNAs, including 10 novel miRNAs, were obtain from the livers by sequencing, and 73 target genes involved in lipid metabolic processes of these miRNAs were found, which constituted 316 miRNA-mRNA pairs. Two miRNA-mRNA pairs including one novel miRNA and one known miRNA, N-miR-16020-FASN and gga-miR-144-ELOVL6, were selected to validate the miRNA-mRNA negative relation. And the results showed that N-mir-16020 and gga-miR-144 could respectively bind the 3'-UTRs of FASN and ELOVL6 to control their expressions. This study provides new sights and useful information for future research on regulation network in duck lipid metabolism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MiR-144 affects fatty acid composition by regulating ELOVL6 expression in duck hepatocytes.Cell Biol Int. 2017 Jun;41(6):691-696. doi: 10.1002/cbin.10753. Epub 2017 Apr 19. Cell Biol Int. 2017. PMID: 28225172
-
Transcriptome analysis of miRNA and mRNA in the livers of pigs with highly diverged backfat thickness.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 14;9(1):16740. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53377-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31727987 Free PMC article.
-
Immune-related miRNA-mRNA regulation network in the livers of DHAV-3-infected ducklings.BMC Genomics. 2020 Feb 4;21(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-6539-7. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32019511 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative roles of microRNAs in lipid metabolism and dyslipidemia.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2019 Jun;30(3):165-171. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000603. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2019. PMID: 30985366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Energizing miRNA research: a review of the role of miRNAs in lipid metabolism, with a prediction that miR-103/107 regulates human metabolic pathways.Mol Genet Metab. 2007 Jul;91(3):209-17. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2007.03.011. Epub 2007 May 22. Mol Genet Metab. 2007. PMID: 17521938 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pre-hatching and post-hatching environmental factors related to epigenetic mechanisms in poultry.J Anim Sci. 2022 Jan 1;100(1):skab370. doi: 10.1093/jas/skab370. J Anim Sci. 2022. PMID: 34932113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of microRNAs during Embryonic Skeletal Muscle Development in the Shan Ma Duck.Animals (Basel). 2020 Aug 14;10(8):1417. doi: 10.3390/ani10081417. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32823859 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen Promotes Hepatic Synthesis of Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids by Regulating ELOVL5 at Post-Transcriptional Level in Laying Hens.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jun 30;18(7):1405. doi: 10.3390/ijms18071405. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28665359 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Conjugated Linoleic Acid Supplementation on the Expression Profile of miRNAs in Porcine Adipose Tissue.Genes (Basel). 2017 Oct 13;8(10):271. doi: 10.3390/genes8100271. Genes (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29027986 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Candidate Genes for Sebum Deposition in Pekin Ducks Using Genome-Wide Association Studies.Genes (Basel). 2024 Nov 29;15(12):1553. doi: 10.3390/genes15121553. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766820 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee R. C., Feinbaum R. L. & Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75, 843–854 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Wightman B., Ha I. & Ruvkun G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell 75, 855–862 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Lee Y. et al. The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature 425, 415–419 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

