Disruption of Slc52a3 gene causes neonatal lethality with riboflavin deficiency in mice
- PMID: 27272163
- PMCID: PMC4897618
- DOI: 10.1038/srep27557
Disruption of Slc52a3 gene causes neonatal lethality with riboflavin deficiency in mice
Abstract
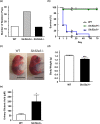
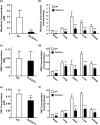
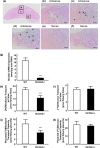
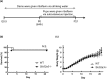
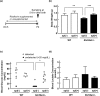
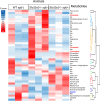
Homeostasis of riboflavin should be maintained by transporters. Previous in vitro studies have elucidated basic information about riboflavin transporter RFVT3 encoded by SLC52A3 gene. However, the contribution of RFVT3 to the maintenance of riboflavin homeostasis and the significance in vivo remain unclear. Here, we investigated the physiological role of RFVT3 using Slc52a3 knockout (Slc52a3-/-) mice. Most Slc52a3-/- mice died with hyperlipidemia and hypoglycemia within 48 hr after birth. The plasma and tissue riboflavin concentrations in Slc52a3-/- mice at postnatal day 0 were dramatically lower than those in wild-type (WT) littermates. Slc52a3-/- fetuses showed a lower capacity of placental riboflavin transport compared with WT fetuses. Riboflavin supplement during pregnancy and after birth reduced neonatal death and metabolic disorders. To our knowledge, this is the first report to indicate that Rfvt3 contributes to placental riboflavin transport, and that disruption of Slc52a3 gene caused neonatal mortality with hyperlipidemia and hypoglycemia owing to riboflavin deficiency.
Figures
References
-
- Depeint F., Bruce W. R., Shangari N., Mehta R. & O’Brien P. J. Mitochondrial function and toxicity: role of the B vitamin family on mitochondrial energy metabolism. Chem Biol Interact 163, 94–112 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Powers H. J. Riboflavin (vitamin B-2) and health. Am J Clin Nutr 77, 1352–1360 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Robitaille J., Carmichael S. L., Shaw G. M. & Olney R. S. Maternal nutrient intake and risks for transverse and longitudinal limb deficiencies: data from the National Birth Defects Prevention Study, 1997–2003. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 85, 773–779 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Smedts H. P. et al. Maternal intake of fat, riboflavin and nicotinamide and the risk of having offspring with congenital heart defects. Eur J Nutr 47, 357–365 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Foraker A. B., Khantwal C. M. & Swaan P. W. Current perspectives on the cellular uptake and trafficking of riboflavin. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 55, 1467–1483 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

