Hyperlipidemia in COPD is associated with decreased incidence of pneumonia and mortality: a nationwide health insurance data-based retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 27274227
- PMCID: PMC4876799
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S102708
Hyperlipidemia in COPD is associated with decreased incidence of pneumonia and mortality: a nationwide health insurance data-based retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Purpose: COPD is often associated with various comorbidities that may influence its outcomes. Pneumonia, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and cancer are the major causes of death in COPD patients. The objective of this study is to investigate the influence of comorbidities on COPD by using the Taiwan National Health Insurance database.
Patients and methods: We retrospectively analyzed the database in 2006 of one million sampling cohort. Newly diagnosed patients with COPD with a controlled cohort that was matched by age, sex, and Charlson comorbidity index (CCI) were included for analysis.
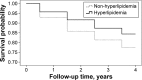
Results: In total, 1,491 patients with COPD were included for analysis (61.8% male). Patients with COPD had higher incidences of pneumonia (25.7% vs 10.4%; P<0.0001), CVD (15.1% vs 10.5%; P<0.0001), and mortality rate (26.6% vs 15.8%; P<0.001) compared with the control group in the 4-year follow-up. In patients with COPD, CCI ≥3 have a higher incidence of pneumonia (hazard ratio [HR] 1.61; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.23-2.09; P<0.0001), CVD (HR 1.73; 95% CI 1.24-2.41; P=0.001), and mortality (HR 1.12; 95% CI 1.12-1.83; P=0.004). Among the major comorbidities of COPD, hyperlipidemia was associated with decreased incidence of pneumonia (HR 0.68; 95% CI 0.5-0.93; P=0.016) and mortality (HR 0.64; 95% CI 0.46-0.90; P=0.009), but was not associated with increased risk of CVD (HR 1.10; 95% CI 0.78-1.55; P=0.588).
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that COPD is associated with increased incidence of pneumonia, CVD, and mortality. In patients with COPD, higher CCI is associated with increased incidence of pneumonia, CVD, and mortality. However, COPD with hyperlipidemia is associated with decreased incidence of pneumonia and mortality.
Keywords: COPD; hyperlipidemia; mortality; pneumonia.
Figures
References
-
- Chen JC, Mannino DM. Worldwide epidemiology of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 1999;5:93–99. - PubMed
-
- Murray CJ, Lopez AD. Alternative projections of mortality and disability by cause 1990–2020: Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. 1997;349:1498–1504. - PubMed
-
- Shirtcliffe P, Weatherall M, Travers J, Beasley R. The multiple dimensions of airways disease: targeting treatment to clinical phenotypes. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2011;17:72–78. - PubMed
-
- Global Strategy for Diagnosis Management, and Prevention of COPD – 2016 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) 2016. [Accessed Feb 17, 2016]. Available from: http://www.goldcopd.com/
-
- Tantucci C. COPD and osteoporosis: something more than a comorbidity. Endocrine. 2012;42:5–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

