Emergency cesarean section in an epidemic of the middle east respiratory syndrome: a case report
- PMID: 27274377
- PMCID: PMC4891544
- DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2016.69.3.287
Emergency cesarean section in an epidemic of the middle east respiratory syndrome: a case report
Abstract
Only a few reports have been published on women with an infectious respiratory viral pathogen, such as Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) Coronavirus delivering a baby. A laboratory confirmed case of MERS was reported during a MERS outbreak in the Republic of Korea in a woman at gestational week 35 + 4. She recovered, and delivered a healthy baby by emergency cesarean section (C-sec). We present the clinical course and the emergency C-sec in a pregnant woman with MERS.
Keywords: Cesarean section; Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus; Pregnant women.
Figures
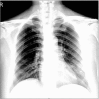
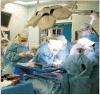

References
-
- Buchholz U, Müller MA, Nitsche A, Sanewski A, Wevering N, Bauer-Balci T, et al. Contact investigation of a case of human novel coronavirus infection treated in a German hospital, October-November 2012. Euro Surveill. 2013;18 - PubMed
-
- Al-Tawfiq JA, Perl TM. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in healthcare settings. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2015;28:392–396. - PubMed
-
- Warning JC, McCracken SA, Morris JM. A balancing act: mechanisms by which the fetus avoids rejection by the maternal immune system. Reproduction. 2011;141:715–724. - PubMed
-
- Boisramé T, Sananès N, Fritz G, Boudier E, Viville B, Aissi G, et al. Abruptio placentae. Diagnosis, management and maternal-fetal prognosis: a retrospective study of 100 cases. Gynecol Obstet Fertil. 2014;42:78–83. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

