Long-term assessment of prostaglandin analogs and timolol fixed combinations vs prostaglandin analogs monotherapy
- PMID: 27275435
- PMCID: PMC4886894
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2016.05.21
Long-term assessment of prostaglandin analogs and timolol fixed combinations vs prostaglandin analogs monotherapy
Abstract
Aim: To draw a Meta-analysis over the comparison of the intraocular pressure (IOP)-lowering efficacy and safety between the commonly used fixed-combinations of prostaglandin analogs and 0.5% timolol with prostaglandin analogs (PGAs) monotherapy.
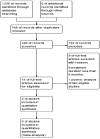
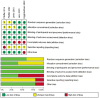
Methods: After searching the published reports from MEDLINE, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library, all randomized controlled clinical trials (RCTs) comparing the fixed combination of PGAs/timolol therapy (FCs) and PGAs monotherapy with treatment duration at least 6mo were included. The efficacy outcomes were mean diurnal IOP, percentage of participants whose IOP were lower than 18 mm Hg, incidence of visual field change, while the safety outcomes included corneal side effects, hyperemia and eye irritation. The analysis was carried out in RevMan version 5.3 software.
Results: After six-month medical intervention, the mean diurnal IOP of FCs was lower than PGAs (MD -1.14, 95% CI -1.82 to -0.46, P=0.001); the percentage of target IOP achieving between FCs and PGAs showed no significant difference (RR 1.18, 95% CI 0.97 to 1.43, P=0.10). No statistically significant differences of the incidence of hyperemia (RR 0.67, 95% CI 0.45 to 1.01, P=0.06) and eye irritation (RR 1.20, 95% CI 0.95 to 1.51, P=0.12) between the FCs and PGAs monotherapy were detected. Only one research involved in corneal events, result of this trial revealed no difference between two intervention groups regarding corneal effects (central endothelial cell density, MD -0.20, 95% CI -0.72 to 0.32, P=0.45; central corneal thickness, MD -0.01, 95% CI -0.02 to 0.00, P=0.23). The evaluation of visual field change was not performed due to the limited duration of the trials included in this Meta-analysis.
Conclusion: The long-term efficacy of the FCs overweighed the PGAs monotherapy in lowering IOP, but in the incidence of hyperemia and eye irritation syndromes, the differences are not statically significant. More RCTs with detailed and authentic data over the assessments of visual functions and morphology of optic nerve heads are hoped to be conducted.
Keywords: bimatoprost; fixed combination of prostaglandin analogs and timolol; latanoprost; ocular hypertension; open angle glaucoma; tafluprost; timolol.
Figures
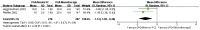
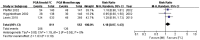

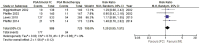
References
-
- Kass MA, Heuer DK, Higginbotham EJ, Johnson CA, Keltner JL, Miller JP, Parrish RK, 2nd, Wilson MR, Gordon MO. The Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study: a randomized trial determines that topical ocular hypotensive medication delays or prevents the onset of primary open-angle glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002;120(6):701–713. - PubMed
-
- Lichter PR, Musch DC, Gillespie BW, Guire KE, Janz NK, Wren PA, Mills RP, CIGTS Study Group Interim clinical outcomes in the Collaborative Initial Glaucoma Treatment Study comparing initial treatment randomized to medications or surgery. Ophthalmology. 2001;108(11):1943–1953. - PubMed
-
- Ammar DA, Noecker RJ, Kahook MY. Effects of benzalkonium chloride-preserved, polyquad-preserved, and sofZia-preserved topical glaucoma medications on human ocular epithelial cells. Adv Ther. 2010;27(11):837–845. - PubMed
-
- Kahook MY, Noecker RJ. Comparison of corneal and conjunctival changes after dosing of travoprost preserved with sofZia, latanoprost with 0.02% benzalkonium chloride, and preservative-free artificial tears. Cornea. 2008;27(3):339–343. - PubMed
-
- Noecker RJ, Herrygers LA, Anwaruddin R. Corneal and conjunctival changes caused by commonly used glaucoma medications. Cornea. 2004;23(5):490–496. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
