Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction attenuates rheumatoid arthritis partially by reversing inflammation-immune system imbalance
- PMID: 27277474
- PMCID: PMC4898408
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-016-0921-x
Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction attenuates rheumatoid arthritis partially by reversing inflammation-immune system imbalance
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction attenuates rheumatoid arthritis partially by reversing inflammation-immune system imbalance.J Transl Med. 2020 Sep 29;18(1):372. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02536-0. J Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32993688 Free PMC article.
Abstract
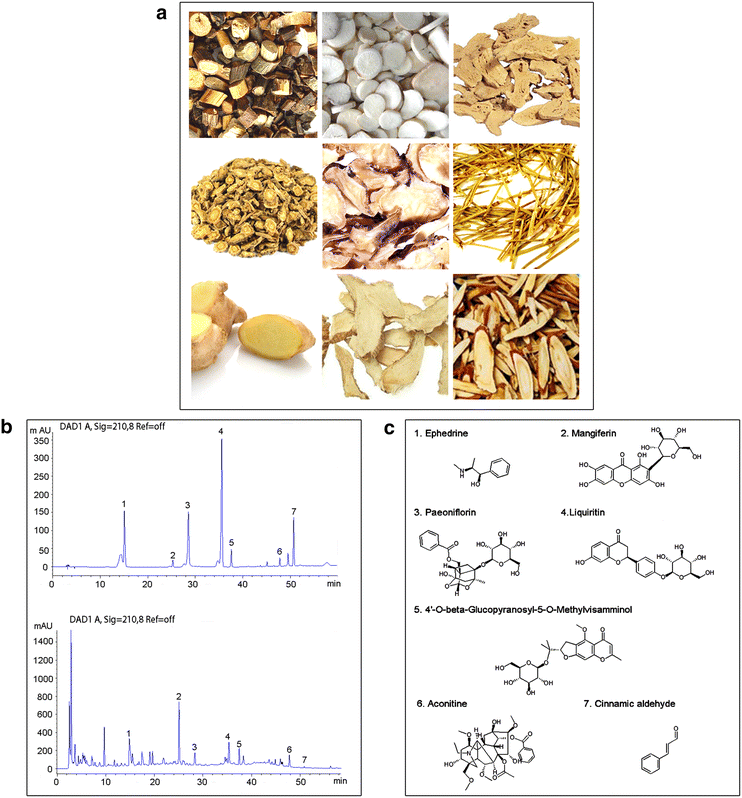
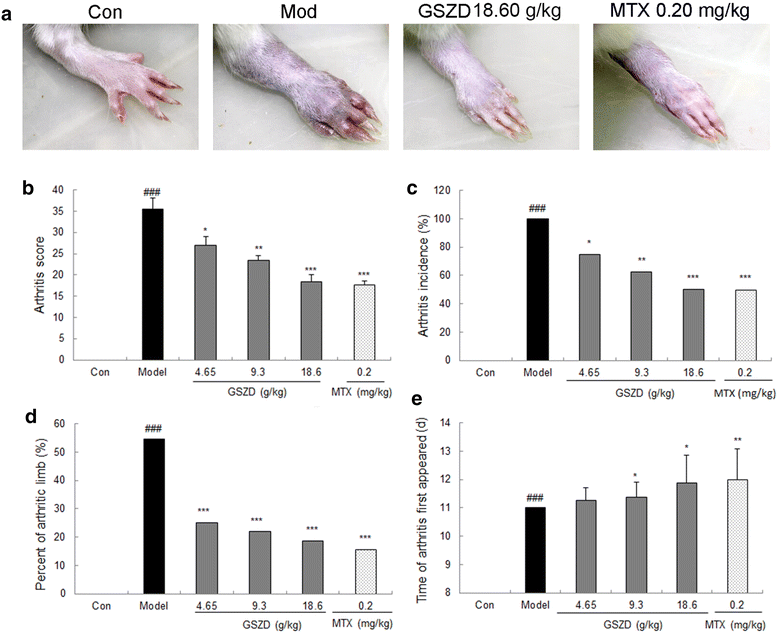
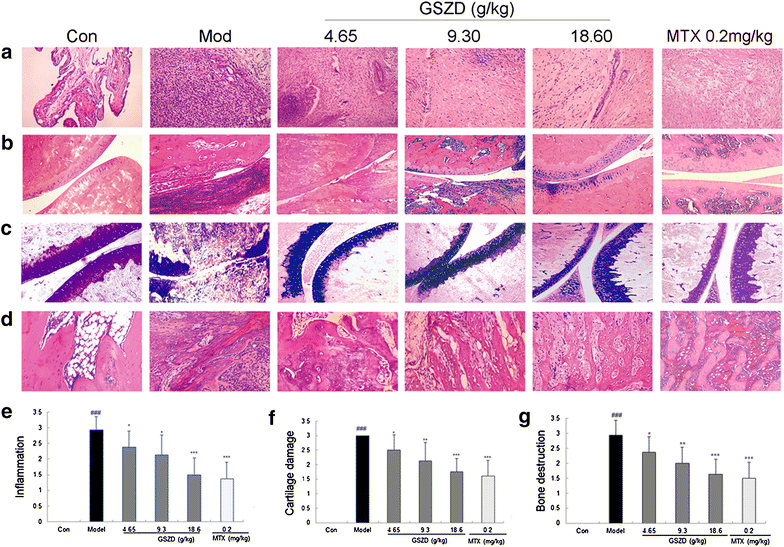
Background: Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction (GSZD) has been extensively used for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) therapy. Marked therapeutic efficacy of GSZD acting on RA has been demonstrated in several long-term clinical trials without any significant side effects. However, its pharmacological mechanisms remain unclear due to a lack of appropriate scientific methodology.
Methods: GSZD's mechanisms of action were investigated using an integrative approach that combined drug target prediction, network analysis, and experimental validation.
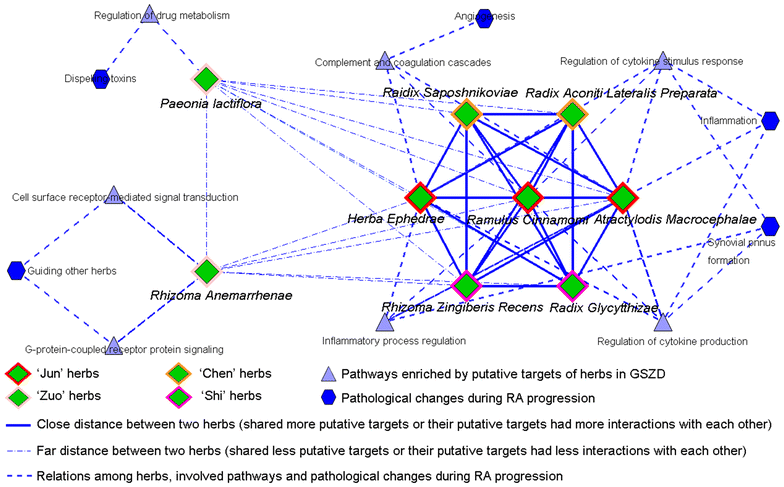
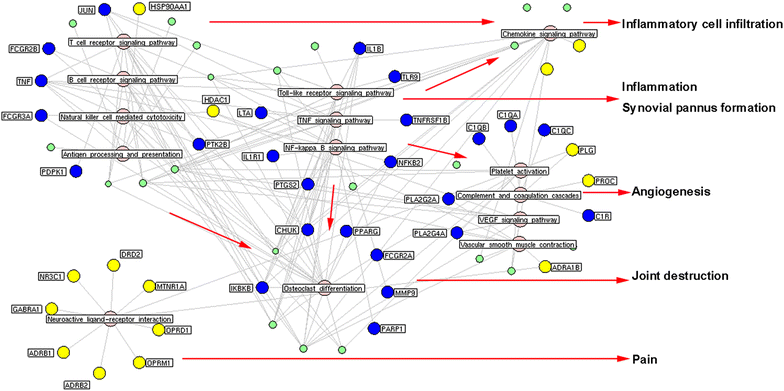
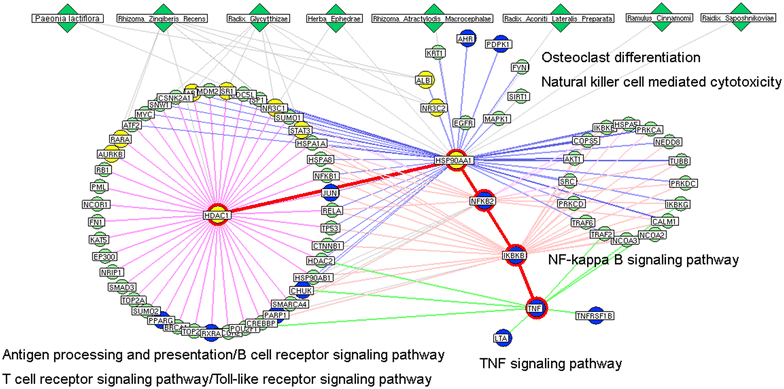
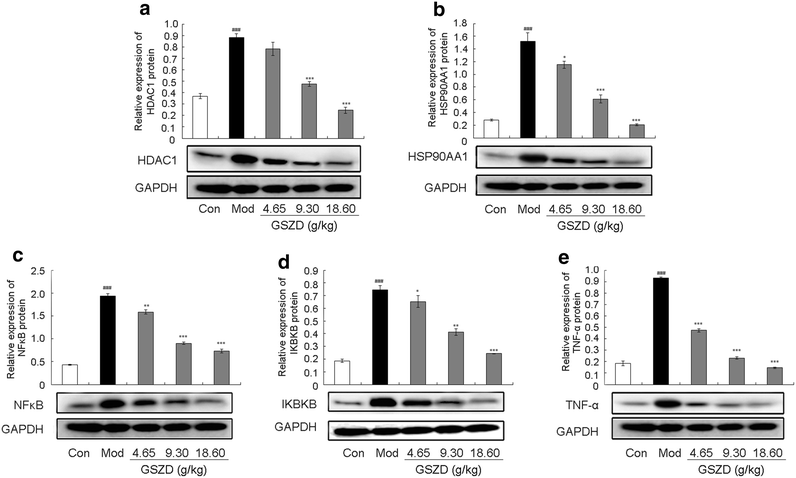
Results: A total of 77 putative targets were identified for 165 assessed chemical components of GSZD. After calculating the topological features of the nodes and edges in the created drug-target network, we identified a candidate GSZD-targeted signal axis that contained interactions between two putative GSZD targets [histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) and heat shock protein 90 kDa alpha, class A member 1 (HSP90AA1)] and three known RA-related targets [NFKB2; inhibitor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells, kinase beta (IKBKB); and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α)]. This signal axis could connect different functional modules that are significantly associated with various RA-related signaling pathways, including T/B cell receptor, Toll-like receptor, NF-kappa B and TNF pathways, as well as osteoclast differentiation. Furthermore, the therapeutic effects and putative molecular mechanisms of GSZD's actions on RA were experimentally validated in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusions: GSZD may partially attenuate RA by reversing inflammation-immune system imbalance and regulating the HDAC1-HSP90AA1-NFKB2-IKBKB-TNF-α signaling axis.
Keywords: Experimental validation; Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction; Network pharmacology; Rheumatoid arthritis; TCM herbal formula.
Figures


References
-
- Urushibara M, Takayanagi H, Koga T, Kim S, Isobe M, Morishita Y, Nakagawa T, Löeffler M, Kodama T, Kurosawa H, Taniguchi T. The antirheumatic drug leflunomide inhibits osteoclastogenesis by interfering with receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand-stimulated induction of nuclear factor of activated T cells c1. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:794–804. doi: 10.1002/art.20206. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

