Cytochrome bd Displays Significant Quinol Peroxidase Activity
- PMID: 27279363
- PMCID: PMC4899803
- DOI: 10.1038/srep27631
Cytochrome bd Displays Significant Quinol Peroxidase Activity
Abstract
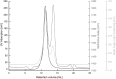
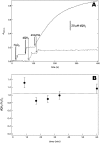
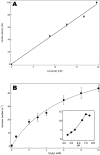
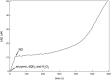
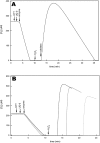
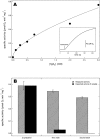
Cytochrome bd is a prokaryotic terminal oxidase that catalyses the electrogenic reduction of oxygen to water using ubiquinol as electron donor. Cytochrome bd is a tri-haem integral membrane enzyme carrying a low-spin haem b558, and two high-spin haems: b595 and d. Here we show that besides its oxidase activity, cytochrome bd from Escherichia coli is a genuine quinol peroxidase (QPO) that reduces hydrogen peroxide to water. The highly active and pure enzyme preparation used in this study did not display the catalase activity recently reported for E. coli cytochrome bd. To our knowledge, cytochrome bd is the first membrane-bound quinol peroxidase detected in E. coli. The observation that cytochrome bd is a quinol peroxidase, can provide a biochemical basis for its role in detoxification of hydrogen peroxide and may explain the frequent findings reported in the literature that indicate increased sensitivity to hydrogen peroxide and decreased virulence in mutants that lack the enzyme.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Junemann S. Cytochrome bd terminal oxidase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1321, 107–127 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Miller M. J. & Gennis R. B. The purification and characterization of the cytochrome d terminal oxidase complex of the Escherichia coli aerobic respiratory chain. J. Biol. Chem. 258, 9159–9165 (1983). - PubMed
-
- Kita K., Konishi K. & Anraku Y. Terminal oxidases of Escherichia coli aerobic respiratory chain. II. Purification and properties of cytochrome b558-d complex from cells grown with limited oxygen and evidence of branched electron-carrying systems. J. Biol. Chem. 259, 3375–3381 (1984). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

