Living to the range limit: consumer isotopic variation increases with environmental stress
- PMID: 27280067
- PMCID: PMC4893340
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.2034
Living to the range limit: consumer isotopic variation increases with environmental stress
Abstract
Background: Theoretically, each species' ecological niche is phylogenetically-determined and expressed spatially as the species' range. However, environmental stress gradients may directly or indirectly decrease individual performance, such that the precise process delimiting a species range may not be revealed simply by studying abundance patterns. In the intertidal habitat the vertical ranges of marine species may be constrained by their abilities to tolerate thermal and desiccation stress, which may act directly or indirectly, the latter by limiting the availability of preferred trophic resources. Therefore, we expected individuals at greater shore heights to show greater variation in diet alongside lower indices of physiological condition.
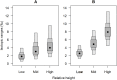
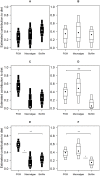
Methods: We sampled the grazing gastropod Echinolittorina peruviana from the desert coastline of northern Chile at three shore heights, across eighteen regionally-representative shores. Stable isotope values (δ13C and δ15N) were extracted from E. peruviana and its putative food resources to estimate Bayesian ellipse area, carbon and nitrogen ranges and diet. Individual physiological condition was tracked by muscle % C and % N.
Results: There was an increase in isotopic variation at high shore levels, where E. peruviana's preferred resource, tide-deposited particulate organic matter (POM), appeared to decrease in dietary contribution, and was expected to be less abundant. Both muscle % C and % N of individuals decreased with height on the shore.
Discussion: Individuals at higher stress levels appear to be less discriminating in diet, likely because of abiotic forcing, which decreases both consumer mobility and the availability of a preferred resource. Abiotic stress might be expected to increase trophic variation in other selective dietary generalist species. Where this coincides with a lower physiological condition may be a direct factor in setting their range limit.
Keywords: Diet; Intertidal; Isotopic niche; Littorinid; Physiological condition; Range limit; Stable isotopes; Stress gradient; Trophic niche width; Trophic variation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Aldridge DW. Reproductive tactics in relation to life-cycle bioenergetics in three natural populations of the freshwater snail, Leptoxis carinata. Ecology. 1982;63(1):196–208. doi: 10.2307/1937044. - DOI
-
- Aldridge DW, Russell-Hunter WD, McMahon RF. Effects of ambient temperature and of temperature acclimation on nitrogen excretion and differential catabolism of protein and nonprotein resources in the intertidal snails, Littorina saxatilis (Olivi) and L. obtusata (L.) Hydrobiologia. 1995;309(1):101–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00014476. - DOI
-
- Austin MP. Continuum concept, ordination methods, and niche theory. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics. 1985;16(1):39–61. doi: 10.1146/annurev.es.16.110185.000351. - DOI
-
- Barnes C, Sweeting CJ, Jennings S, Barry JT, Polunin NVC. Effect of temperature and ration size on carbon and nitrogen stable isotope trophic fractionation. Functional Ecology. 2007;21(2):356–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2435.2006.01224.x. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

