Implications of supportive and unsupportive behavior for couples with newly diagnosed diabetes
- PMID: 27280364
- PMCID: PMC5033701
- DOI: 10.1037/hea0000388
Implications of supportive and unsupportive behavior for couples with newly diagnosed diabetes
Abstract
Objective: To examine the relation between daily diary reports of diabetes-specific social interactions to patient and partner mood and patient self-care behaviors, and whether relations are moderated by unmitigated communion.
Method: Participants were 70 couples in which 1 person had been diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes in the past 3 years. They were interviewed in-person at baseline and completed daily diary reports on an iPad. Daily diary questionnaires measured support, mood, and self-care behavior (patients only). Unmitigated communion, a personality trait characterized by an overinvolvement in others to the exclusion of the self, was measured at baseline.
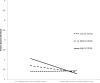
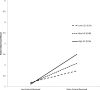
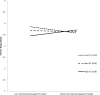
Results: Multilevel statistical modeling revealed that daily fluctuations in partner emotional support were related to daily fluctuations in happy mood, more exercise, and dietary compliance. Partner controlling behavior was related to poor mood but was unrelated to self-care. Relations of support and controlling behavior to mood were strongest for individuals high (vs. low) in unmitigated communion.
Conclusion: Patients newly diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes who felt understood and cared for by partners reported a better mood and were more likely to take care of themselves on a daily basis, whereas patients whose partners were controlling on a daily basis reported poorer mood. Patients characterized by unmitigated communion were most affected by partner supportive and unsupportive behavior. (PsycINFO Database Record
(c) 2016 APA, all rights reserved).
Figures
References
-
- Berg CA, Upchurch R. A developmental-contextual model of couples coping with chronic illness across the adult life span. Psychological Bulletin. 2007;133(6):920–954. - PubMed
-
- Bolger N, Davis A, Rafaeli E. Diary methods: Capturing life as it is lived. Annual Review of Psychology. 2003;54(1):579–616. - PubMed
-
- Bolger N, Laurenceau J-P. Intensive longitudinal methods: An introduction to diary and experience sampling research. Guilford Press; New York, NY: 2013.
-
- Bolger N, Zuckerman A, Kessler RC. Invisible support and adjustment to stress. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 2000;79(6):953–961. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

