Low Density Lipoprotein-Receptor Related Protein 1 Is Differentially Expressed by Neuronal and Glial Populations in the Developing and Mature Mouse Central Nervous System
- PMID: 27280679
- PMCID: PMC4900551
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155878
Low Density Lipoprotein-Receptor Related Protein 1 Is Differentially Expressed by Neuronal and Glial Populations in the Developing and Mature Mouse Central Nervous System
Abstract
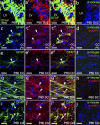
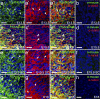
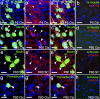
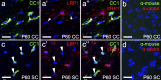
The low density lipoprotein-receptor related protein 1 (LRP1) is a large endocytic cell surface receptor that is known to interact with a variety of ligands, intracellular adaptor proteins and other cell surface receptors to regulate cellular behaviours ranging from proliferation to cell fate specification, migration, axon guidance, and lipid metabolism. A number of studies have demonstrated that LRP1 is expressed in the brain, yet it is unclear which central nervous system cell types express LRP1 during development and in adulthood. Herein we undertake a detailed study of LRP1 expression within the mouse brain and spinal cord, examining a number of developmental stages ranging from embryonic day 13.5 to postnatal day 60. We report that LRP1 expression in the brain peaks during postnatal development. On a cellular level, LRP1 is expressed by radial glia, neuroblasts, microglia, oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs), astrocytes and neurons, with the exception of parvalbumin+ interneurons in the cortex. Most cell populations exhibit stable expression of LRP1 throughout development; however, the proportion of OPCs that express LRP1 increases significantly from ~69% at E15.5 to ~99% in adulthood. We also report that LRP1 expression is rapidly lost as OPCs differentiate, and is absent from all oligodendrocytes, including newborn oligodendrocytes. While LRP1 function has been primarily examined in mature neurons, these expression data suggest it plays a more critical role in glial cell regulation-where expression levels are much higher.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







References
-
- Li Y, Marzolo MP, van Kerkhof P, Strous GJ, Bu G. The YXXL motif, but not the two NPXY motifs, serves as the dominant endocytosis signal for low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. Journal of Biological Chemistry. American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology; 2000;275: 17187–17194. 10.1074/jbc.M000490200 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gopal U, Bohonowych JE, Lema-Tome C, Liu A, Garrett-Mayer E, Wang B, et al. A Novel Extracellular Hsp90 Mediated Co-Receptor Function for LRP1 Regulates EphA2 Dependent Glioblastoma Cell Invasion. Lesniak M, editor. PLoS ONE. Public Library of Science; 2011; e17649. 10.1371/journal.pone.0017649 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

