In vivo confocal microscopy of meibomian glands in primary blepharospasm: A prospective case-control study in a Chinese population
- PMID: 27281086
- PMCID: PMC4907664
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003833
In vivo confocal microscopy of meibomian glands in primary blepharospasm: A prospective case-control study in a Chinese population
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Medicine, Volume 95, Issue 23: Erratum.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Jul 18;95(28):e0916. doi: 10.1097/01.md.0000489580.04709.16. eCollection 2016 Jul. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 31265603 Free PMC article.
Abstract
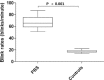
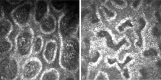
The aim of the study was to evaluate the morphological changes of meibomian glands (MGs) in primary blepharospasm (PBS) by in vivo laser scanning confocal microscopy (LSCM) and to investigate the correlations between clinical data of PBS and LSCM parameters of MGs. This prospective and case-control study recruited 30 consecutive PBS patients and 30 age- and gender-matched healthy controls. After questionnaire assessments of ocular surface disease index (OSDI), Jankovic rating scale, and blepharospasm disability index, all subjects underwent blink rate evaluation, tear film break-up time (TBUT), corneal fluorescein staining (CFS), Schirmer test, MG expressibility, meibum quality, MG dropout, and LSCM examination of the MGs. The main LSCM outcomes included the mean MG acinar area and density, orifice diameter, meibum secretion reflectivity, acinar irregularity, and inhomogeneity of interstice and acinar wall. The PBS patients had significantly higher blink rate, higher OSDI and CFS scores, lower TBUT and Schirmer test value, and worse MG expressibility than the controls (All P < 0.05), whereas meibum quality showed no difference (P > 0.05). The PBS patients showed lower values of MG acinar area, orifice diameter and meibum secretion reflectivity, and higher scores of acinar irregularity and inhomogeneity of interstices than the controls (All P < 0.05). For the PBS patients, the severity of blepharospasm evaluated by JCR scale was strong correlated with MG acinar area (P < 0.001), orifice diameter (P = 0.002), meibum secretion reflectivity (P = 0.002), and MG acinar irregularity (P = 0.013). The MG expressibility was significantly correlated to MG acinar area (P = 0.039), orifice diameter (P < 0.001), and MG acinar irregularity (P = 0.014). The OSDI score was moderate correlated with MG acinar irregularity (P = 0.016), whereas the TBUT value was positively correlated with MG acinar area (P = 0.045) and negatively correlated to MG acinar irregularity (P = 0.016). The CFS score was negatively correlated to MG orifice diameter (P = 0.008). The LSCM provided a noninvasive tool for in vivo histopathologic studies of MGs in PBS patients. The excessive constriction of lid muscles closely related to MG morphological alterations of PBS, which offered a new research approach to interpret the interactional mechanism between dry eye and PBS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interests to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Hallett M. Blepharospasm: recent advances. Neurology 2002; 59:1306–1312. - PubMed
-
- Jankovic J, Orman J. Blepharospasm: demographic and clinical survey of 250 patients. Ann Ophthalmol 1984; 16:371–376. - PubMed
-
- Lindeboom R, De Haan R, Aramideh M, et al. The Blepharospasm Disability Scale: an instrument for the assessment of functional health in blepharospasm. Mov Disord 1995; 10:444–449. - PubMed
-
- Defazio G, Abbruzzese G, Aniello MS, et al. Eye symptoms in relatives of patients with primary adult-onset dystonia. Mov Disord 2012; 27:305–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

