The bacterial DnaA-trio replication origin element specifies single-stranded DNA initiator binding
- PMID: 27281207
- PMCID: PMC4913881
- DOI: 10.1038/nature17962
The bacterial DnaA-trio replication origin element specifies single-stranded DNA initiator binding
Erratum in
-
Erratum: The bacterial DnaA-trio replication origin element specifies single-stranded DNA initiator binding.Nature. 2016 Aug 25;536(7617):488. doi: 10.1038/nature18932. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27362230 No abstract available.
Abstract
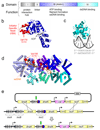
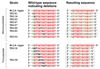
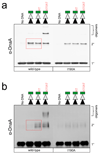
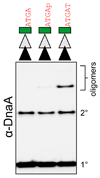
DNA replication is tightly controlled to ensure accurate inheritance of genetic information. In all organisms, initiator proteins possessing AAA+ (ATPases associated with various cellular activities) domains bind replication origins to license new rounds of DNA synthesis. In bacteria the master initiator protein, DnaA, is highly conserved and has two crucial DNA binding activities. DnaA monomers recognize the replication origin (oriC) by binding double-stranded DNA sequences (DnaA-boxes); subsequently, DnaA filaments assemble and promote duplex unwinding by engaging and stretching a single DNA strand. While the specificity for duplex DnaA-boxes by DnaA has been appreciated for over 30 years, the sequence specificity for single-strand DNA binding has remained unknown. Here we identify a new indispensable bacterial replication origin element composed of a repeating trinucleotide motif that we term the DnaA-trio. We show that the function of the DnaA-trio is to stabilize DnaA filaments on a single DNA strand, thus providing essential precision to this binding mechanism. Bioinformatic analysis detects DnaA-trios in replication origins throughout the bacterial kingdom, indicating that this element is part of the core oriC structure. The discovery and characterization of the novel DnaA-trio extends our fundamental understanding of bacterial DNA replication initiation, and because of the conserved structure of AAA+ initiator proteins these findings raise the possibility of specific recognition motifs within replication origins of higher organisms.
Figures





Similar articles
-
DNA stretching by bacterial initiators promotes replication origin opening.Nature. 2011 Oct 2;478(7368):209-13. doi: 10.1038/nature10455. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21964332 Free PMC article.
-
The bacterial replication origin BUS promotes nucleobase capture.Nat Commun. 2023 Dec 14;14(1):8339. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43823-w. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38097584 Free PMC article.
-
Thermotoga maritima oriC involves a DNA unwinding element with distinct modules and a DnaA-oligomerizing region with a novel directional binding mode.J Biol Chem. 2023 Jul;299(7):104888. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104888. Epub 2023 Jun 3. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37276959 Free PMC article.
-
How bacteria initiate DNA replication comes into focus.Bioessays. 2025 Jan;47(1):e2400151. doi: 10.1002/bies.202400151. Epub 2024 Oct 10. Bioessays. 2025. PMID: 39390825 Review.
-
Regulating DNA replication in bacteria.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Apr 1;5(4):a012922. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012922. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23471435 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unique and Universal Features of Epsilonproteobacterial Origins of Chromosome Replication and DnaA-DnaA Box Interactions.Front Microbiol. 2016 Sep 30;7:1555. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01555. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27746772 Free PMC article.
-
Origin DNA Melting-An Essential Process with Divergent Mechanisms.Genes (Basel). 2017 Jan 11;8(1):26. doi: 10.3390/genes8010026. Genes (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28085061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DoriC 10.0: an updated database of replication origins in prokaryotic genomes including chromosomes and plasmids.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jan 8;47(D1):D74-D77. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1014. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30364951 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and Function of the Campylobacter jejuni Chromosome Replication Origin.Front Microbiol. 2018 Jul 12;9:1533. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01533. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30050516 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking, Bending, and Binding: Regulation of Initiation of Chromosome Replication During the Escherichia coli Cell Cycle by Transcriptional Modulators That Interact With Origin DNA.Front Microbiol. 2021 Sep 20;12:732270. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.732270. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34616385 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Messer W. The bacterial replication initiator DnaA. DnaA and oriC, the bacterial mode to initiate DNA replication. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2002;26:355–374. - PubMed
-
- Fuller RS, Funnell BE, Kornberg A. The dnaA protein complex with the E. coli chromosomal replication origin (oriC) and other DNA sites. Cell. 1984;38:889–900. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

