VNN1 promotes atherosclerosis progression in apoE-/- mice fed a high-fat/high-cholesterol diet
- PMID: 27281478
- PMCID: PMC4959856
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M065565
VNN1 promotes atherosclerosis progression in apoE-/- mice fed a high-fat/high-cholesterol diet
Abstract
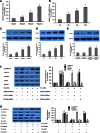
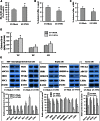
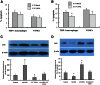
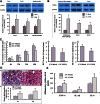
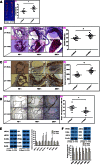
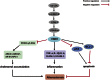
Accumulated evidence shows that vanin-1 (VNN1) plays a key part in glucose metabolism. We explored the effect of VNN1 on cholesterol metabolism, inflammation, apoptosis in vitro, and progression of atherosclerotic plaques in apoE(-/-) mice. Oxidized LDL (Ox-LDL) significantly induced VNN1 expression through an ERK1/2/cyclooxygenase-2/PPARα signaling pathway. VNN1 significantly increased cellular cholesterol content and decreased apoAI and HDL-cholesterol (HDL-C)-mediated efflux by 25.16% and 23.13%, respectively, in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells (P < 0.05). In addition, VNN1 attenuated Ox-LDL-induced apoptosis through upregulation of expression of p53 by 59.15% and downregulation of expression of B-cell lymphoma-2 127.13% in THP-1 macrophage (P < 0.05). In vivo, apoE(-/-) mice were divided randomly into two groups and transduced with lentivirus (LV)-Mock or LV-VNN1 for 12 weeks. VNN1-treated mice showed increased liver lipid content and plasma levels of TG (124.48%), LDL-cholesterol (119.64%), TNF-α (148.74%), interleukin (IL)-1β (131.81%), and IL-6 (156.51%), whereas plasma levels of HDL-C (25.75%) were decreased significantly (P < 0.05). Consistent with these data, development of atherosclerotic lesions was increased significantly upon infection of apoE(-/-) mice with LV-VNN1. These observations suggest that VNN1 may be a promising therapeutic candidate against atherosclerosis.
Keywords: apolipoprotein E; inflammation; oxidized low density lipoprotein; vanin-1.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Annema W., and von Eckardstein A.. 2013. High-density lipoproteins. Multifunctional but vulnerable protections from atherosclerosis. Circ. J. 77: 2432–2448. - PubMed
-
- Hu Y. W., Hu Y. R., Zhao J. Y., Li S. F., Ma X., Wu S. G., Lu J. B., Qiu Y. R., Sha Y. H., Wang Y. C., et al. . 2014. An agomir of miR-144–3p accelerates plaque formation through impairing reverse cholesterol transport and promoting pro-inflammatory cytokine production. PLoS One. 9: e94997. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Packard R. R., and Libby P.. 2008. Inflammation in atherosclerosis: from vascular biology to biomarker discovery and risk prediction. Clin. Chem. 54: 24–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

