The Roles of Type I Interferon in Bacterial Infection
- PMID: 27281568
- PMCID: PMC5847370
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2016.05.016
The Roles of Type I Interferon in Bacterial Infection
Abstract
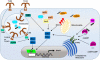
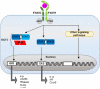
Type I interferons (IFNs) are pleiotropic cytokines well recognized for their role in the induction of a potent antiviral gene program essential for host defense against viruses. They also modulate innate and adaptive immune responses. However, the role of type I IFNs in host defense against bacterial infections is enigmatic. Depending on the bacterium, they exert seemingly opposite and capricious functions. In this review, we summarize the effect of type I IFNs on specific bacterial infections and highlight the effector mechanisms regulated by type I IFNs in an attempt to elucidate new avenues to understanding their role.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Ang DKY, Oates CVL, Schuelein R, Kelly M, Sansom FM, Bourges D, Boon L, et al. Cutting edge: pulmonary Legionella pneumophila is controlled by plasmacytoid dendritic cells but not type I IFN. Journal of Immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2010;184(10):5429–33. - PubMed
-
- Bergstrom B, Aune MH, Awuh J. a., Kojen JF, Blix KJ, Ryan L, Flo TH, et al. TLR8 Senses Staphylococcus aureus RNA in Human Primary Monocytes and Macrophages and Induces IFN-Production via a TAK1-IKK -IRF5 Signaling Pathway. The Journal of Immunology. 2015;195(3) doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1403176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

