LTBP2 is a prognostic marker in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 27281608
- PMCID: PMC5216705
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.8855
LTBP2 is a prognostic marker in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
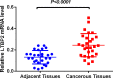
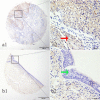
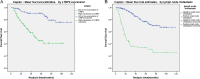
Latent transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta binding protein 2 (LTBP2) belongs to the fibrillin/LTBP extracellular matrix glycoprotein superfamily. It plays vital roles in tumorigenesis through regulating TGFβ activity, elastogenesis and maintenance of the extracellular matrix (ECM) structure. In this study, we determined the expression levels of LTBP2 mRNA and protein in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) tissues and adjacent normal tissues by quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) and tissue microarray immunohistochemistry analysis (TMA-IHC) respectively. LTBP2 protein levels in cancer tissues were correlated with HNSCC patients' clinical characteristics and overall survival. Both LTBP2 mRNA and protein levels were significantly higher in HNSCC tissues than in adjacent normal tissues. High LTBP2 protein level was associated with lymph node metastasis and higher pTNM stages. High LTBP2 protein level is an independent prognostic marker in HNSCC. Our data suggest that LTBP2 acts as an oncogene in HNSCC development and progression. Detection of LTBP2 expression could be a useful prognosis marker and targeting LTBP2 may represent a novel strategy for cancer treatment through regulating activities of TGFβ.
Keywords: LTBP2; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; immunohistochemistry; prognosis; qPCR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Elevated expression of iASPP in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and its clinical significance.Med Oncol. 2012 Dec;29(5):3381-8. doi: 10.1007/s12032-012-0306-9. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Med Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22815155
-
Increased expression of miR-93 is associated with poor prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2015 May;36(5):3949-56. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3038-6. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25578493 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway activation on the prognosis of patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinomas.Oncotarget. 2016 May 17;7(20):29780-93. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8957. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27119232 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Insulin Receptor Substrate 1 Expression in the Prognosis of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Oncology. 2025;103(3):253-264. doi: 10.1159/000541004. Epub 2024 Aug 26. Oncology. 2025. PMID: 39186927
-
Impact of tumor budding in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis.Head Neck. 2019 Feb;41(2):542-550. doi: 10.1002/hed.25462. Epub 2018 Dec 14. Head Neck. 2019. PMID: 30549142
Cited by
-
Expression and clinical significance of latent-transforming growth factor beta-binding protein 2 in primary hepatocellular carcinoma.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Sep;98(39):e17216. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000017216. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31574831 Free PMC article.
-
Latent Transforming Growth Factor β Binding Protein 2 (LTBP2) as a Novel Biomarker for the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Pancreatic Carcinoma.Med Sci Monit. 2017 Jul 3;23:3232-3239. doi: 10.12659/msm.905284. Med Sci Monit. 2017. PMID: 28669978 Free PMC article.
-
Arterial spin labeling perfusion-weighted MR imaging: correlation of tumor blood flow with pathological degree of tumor differentiation, clinical stage and nodal metastasis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018 May;275(5):1301-1307. doi: 10.1007/s00405-018-4950-3. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018. PMID: 29582174
-
LTBP2 Knockdown Promotes Ferroptosis in Gastric Cancer Cells through p62-Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Aug 4;2022:6532253. doi: 10.1155/2022/6532253. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35968244 Free PMC article.
-
High Expression of LTBP2 Contributes to Poor Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer Patients and Correlates with the Mesenchymal Colorectal Cancer Subtype.Dis Markers. 2019 Mar 10;2019:5231269. doi: 10.1155/2019/5231269. eCollection 2019. Dis Markers. 2019. PMID: 30956730 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
-
- Wyss A, Hashibe M, Chuang SC, Lee YC, Zhang ZF, Yu GP, Winn DM, Wei Q, Talamini R, Szeszenia-Dabrowska N, Sturgis EM, Smith E, Shangina O, et al. Cigarette, cigar, and pipe smoking and the risk of head and neck cancers: pooled analysis in the International Head and Neck Cancer Epidemiology Consortium. Am J Epidemiol. 2013;178:679–690. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sankaranarayanan R, Masuyer E, Swaminathan R, Ferlay J, Whelan S. Head and neck cancer: a global perspective on epidemiology and prognosis. Anticancer Res. 1998;18:4779–4786. - PubMed
-
- Raghupathy R, Hui EP, Chan AT. Epstein-Barr virus as a paradigm in nasopharyngeal cancer: from lab to clinic. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2014:149–153. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Ren JS, Masuyer E, Ferlay J. Global estimates of cancer prevalence for 27 sites in the adult population in 2008. Int J Cancer. 2013;132:1133–1145. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

