Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality Risk in Patients with Advanced CKD
- PMID: 27281698
- PMCID: PMC4934843
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.10441015
Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality Risk in Patients with Advanced CKD
Abstract
Background and objectives: The high risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and premature death in patients with CKD associates with a plethora of elevated circulating biomarkers that may reflect distinct signaling pathways or simply, are epiphenomena of CKD. We compared the predictive strength of 12 biomarkers analyzed concomitantly in patients with stage 5 CKD.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: From 1994 to 2014, 543 patients with stage 5 CKD (median age =56 years old; 63% men; 199 patients had CVD) took part in our study on malnutrition, inflammation, and CVD in incident dialysis patients. Circulating levels of albumin, ferritin, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), IGF-1, IL-6, orosomucoid, troponin T (TnT), TNF, soluble intracellular adhesion molecule, soluble vascular cellular adhesion molecule 1 (sVCAM-1), and platelet and white blood cell (WBC) counts were analyzed as predictors of the presence of clinically overt CVD at baseline, protein-energy wasting (PEW), and subsequent all-cause mortality. During follow-up for a median of 28 months, there were 149 deaths, 81 of which were caused by CVD.
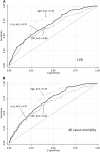
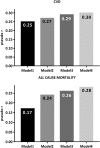
Results: Most biomarkers were elevated compared with reference values and--except for albumin, ferritin, and IGF-1-higher in patients with CVD. In receiver operating characteristic analysis, age, IL-6, TnT, hsCRP, and IGF-1 were classifiers of baseline CVD and predictors of all-cause mortality. In addition to age, diabetes mellitus, smoking (for CVD), and PEW, only IL-6, relative risk (RR) 1.10 and 95% confidence interval ([95% CI], 1.02 to 1.19), sVCAM-1 RR 1.09 (95% CI, 1.01 to 1.17), and serum albumin RR 0.89 (95% CI, 0.83 to 0.95) associated with baseline CVD, and only WBC, hazard ratio (HR) 1.94 (95% CI, 1.34 to 2.82), IL-6 HR 1.79 (95% CI, 1.20 to 2.67), and TNF HR 0.65 (95% CI, 0.44 to 0.97) predicted all-cause mortality.
Conclusions: In addition to age and comorbidities, only IL-6, sVCAM-1, and albumin could-independently of other biomarkers-classify clinical CVD, and only IL-6, WBC, and TNF could-independently of other biomarkers-predict all-cause mortality risk. These data underscore the robustness of IL-6 as a classifier of clinically overt CVD and predictor of all-cause mortality in patients with stage 5 CKD.
Keywords: Biomarkers; C-Reactive Protein; Follow-Up Studies; Humans; Inflammation; Interleukin-6; Renal Insufficiency, Chronic; cardiovascular disease; chronic kidney disease; mortality.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- Fried LF, Shlipak MG, Crump C, Bleyer AJ, Gottdiener JS, Kronmal RA, Kuller LH, Newman AB: Renal insufficiency as a predictor of cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in elderly individuals. J Am Coll Cardiol 41: 1364–1372, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Kooman JP, Kotanko P, Schols AM, Shiels PG, Stenvinkel P: Chronic kidney disease and premature ageing. Nat Rev Nephrol 10: 732–742, 2014 - PubMed
-
- Levin A, Foley RN: Cardiovascular disease in chronic renal insufficiency. Am J Kidney Dis 36[Suppl 3]: S24–S30, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Menon V, Gul A, Sarnak MJ: Cardiovascular risk factors in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 68: 1413–1418, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Ross R: Atherosclerosis--an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 340: 115–126, 1999 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

