Limited Effect of Rebamipide in Addition to Proton Pump Inhibitor (PPI) in the Treatment of Post-Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection Gastric Ulcers: A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing PPI Plus Rebamipide Combination Therapy with PPI Monotherapy
- PMID: 27282261
- PMCID: PMC5087931
- DOI: 10.5009/gnl15486
Limited Effect of Rebamipide in Addition to Proton Pump Inhibitor (PPI) in the Treatment of Post-Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection Gastric Ulcers: A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing PPI Plus Rebamipide Combination Therapy with PPI Monotherapy
Abstract
Background/aims: The ability of endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) to resect large early gastric cancers (EGCs) results in the need to treat large artificial gastric ulcers. This study assessed whether the combination therapy of rebamipide plus a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) offered benefits over PPI monotherapy.
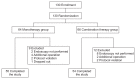
Methods: In this prospective, randomized, multicenter, open-label, and comparative study, patients who had undergone ESD for EGC or gastric adenoma were randomized into groups receiving either rabeprazole monotherapy (10 mg/day, n=64) or a combination of rabeprazole plus rebamipide (300 mg/day, n=66). The Scar stage (S stage) ratio after treatment was compared, and factors independently associated with ulcer healing were identified by using multivariate analyses.
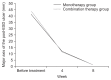
Results: The S stage rates at 4 and 8 weeks were similar in the two groups, even in the subgroups of patients with large amounts of tissue resected and regardless of CYP2C19 genotype. Independent factors for ulcer healing were circumferential location of the tumor and resected tissue size; the type of treatment did not affect ulcer healing.
Conclusions: Combination therapy with rebamipide and PPI had limited benefits compared with PPI monotherapy in the treatment of post-ESD gastric ulcer (UMIN Clinical Trials Registry, UMIN000007435).
Keywords: Antiulcer agents; Endoscopy; Proton pump inhibitors; Stomach ulcer; Therapeutics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A randomized controlled trial of rebamipide plus rabeprazole for the healing of artificial ulcers after endoscopic submucosal dissection.J Gastroenterol. 2011 May;46(5):595-602. doi: 10.1007/s00535-011-0372-3. Epub 2011 Feb 26. J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21359522 Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of short-term proton pump inhibitor plus anti-ulcer drug on the healing of endoscopic submucosal dissection-derived artificial ulcer: a randomized controlled trial.Hepatogastroenterology. 2015 Jan-Feb;62(137):219-24. Hepatogastroenterology. 2015. PMID: 25911899 Clinical Trial.
-
Can rebamipide and proton pump inhibitor combination therapy promote the healing of endoscopic submucosal dissection-induced ulcers? A randomized, prospective, multicenter study.Gastrointest Endosc. 2012 Apr;75(4):739-47. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2011.11.004. Epub 2012 Jan 26. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012. PMID: 22281110 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) plus rebamipide for endoscopic submucosal dissection-induced ulcers: a meta-analysis.Intern Med. 2014;53(12):1243-8. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.53.2160. Epub 2014 Jun 15. Intern Med. 2014. PMID: 24930641 Review.
-
Role of mucoprotective agents in endoscopic submucosal dissection-derived ulcers: A systematic review.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Dec;33(12):1948-1955. doi: 10.1111/jgh.14305. Epub 2018 Jun 25. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29870582
Cited by
-
Clinical Practice Guideline for Endoscopic Resection of Early Gastrointestinal Cancer.Clin Endosc. 2020 Mar;53(2):142-166. doi: 10.5946/ce.2020.032. Epub 2020 Mar 30. Clin Endosc. 2020. PMID: 32252507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is a proton-pump inhibitor necessary after endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial esophageal neoplasms? A propensity score analysis.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2020 Nov 24;13:1756284820974908. doi: 10.1177/1756284820974908. eCollection 2020. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 33281938 Free PMC article.
-
A Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Rebamipide Plus Lansoprazole for the Treatment of Postendoscopic Submucosal Dissection Ulcers.Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2019 Jan;10(1):e00008. doi: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000008. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30702488 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing the Effects of Vonoprazan Plus Rebamipide and Esomeprazole Plus Rebamipide on Gastric Ulcer Healing Induced by Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection.Intern Med. 2019 Jan 15;58(2):159-166. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1146-18. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Intern Med. 2019. PMID: 30210115 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Outcome and risk factors of ulcer healing after gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection: A systematic review and meta-analysis.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2024 Nov 27;16(11):3568-3577. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i11.3568. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2024. PMID: 39649187 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Uedo N, Takeuchi Y, Yamada T, et al. Effect of a proton pump inhibitor or an H2-receptor antagonist on prevention of bleeding from ulcer after endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:1610–1616. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01197.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous