ISPD Peritonitis Recommendations: 2016 Update on Prevention and Treatment
- PMID: 27282851
- PMCID: PMC5033625
- DOI: 10.3747/pdi.2016.00078
ISPD Peritonitis Recommendations: 2016 Update on Prevention and Treatment
Erratum in
-
ISPD Peritonitis Recommendations: 2016 Update on Prevention and Treatment.Perit Dial Int. 2018 Jul-Aug;38(4):313. doi: 10.3747/pdi.2018.00030. Perit Dial Int. 2018. PMID: 29987070 No abstract available.
Keywords: ISPD; Peritonitis; guidelines; prevention; treatment.
Figures
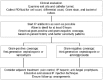

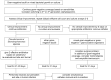
Comment in
-
The 2016 ISPD Update on Prevention and Treatment of Peritonitis-Grading the Evidence.Perit Dial Int. 2016 Sep 10;36(5):469-70. doi: 10.3747/pdi.2016.00118. Perit Dial Int. 2016. PMID: 27659924 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Rising to the Challenge of Antimicrobial Resistance.Perit Dial Int. 2017 Mar-Apr;37(2):129-130. doi: 10.3747/pdi.2016.00277. Perit Dial Int. 2017. PMID: 28360362 No abstract available.
-
Response Letter to the "ISPD Peritonitis Recommendations: 2016 Update on Prevention and Treatment".Perit Dial Int. 2017 Sep-Oct;37(5):584-585. doi: 10.3747/pdi.2017.00055. Perit Dial Int. 2017. PMID: 28931701 No abstract available.
-
Should We Use Adenosine Deaminase Assay for the Differential Diagnosis of Tuberculous Peritonitis in CAPD Patients?Perit Dial Int. 2018 Mar-Apr;38(2):153. doi: 10.3747/pdi.2017.00174. Perit Dial Int. 2018. PMID: 29563278 No abstract available.
-
Inconsistencies in ISPD Peritonitis Recommendations: 2016 Update on Prevention and Treatment and The ISPD Catheter-Related Infection Recommendations: 2017 Update.Perit Dial Int. 2018 Jul-Aug;38(4):309-310. doi: 10.3747/pdi.2018.00026. Perit Dial Int. 2018. PMID: 29987068 No abstract available.
-
Concerns Regarding Inconsistencies Within and Between ISPD Recommendations for Peritonitis and Catheter-Related Infections-In Reply.Perit Dial Int. 2018 Jul-Aug;38(4):311-312. doi: 10.3747/pdi.2018.00046. Perit Dial Int. 2018. PMID: 29987069 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ghali JR, Bannister KM, Brown FG, Rosman JB, Wiggins KJ, Johnson DW, McDonald SP. Microbiology and outcomes of peritonitis in Australian peritoneal dialysis patients. Perit Dial Int 2011; 31:651–62. - PubMed
-
- Pérez Fontan M, Rodríguez-Carmona A, García-Naveiro R, Rosales M, Villaverde P, Valdés F. Peritonitis-related mortality in patients undergoing chronic peritoneal dialysis. Perit Dial Int 2005; 25:274–84. - PubMed
-
- Davenport A. Peritonitis remains the major clinical complication of peritoneal dialysis: the London, UK, peritonitis audit 2002-2003. Perit Dial Int 2009; 29:297–302. - PubMed
-
- Szeto CC, Wong TY, Chow KM, Leung CB, Li PK. Are peritoneal dialysis patients with and without residual renal function equivalent for survival study? Insight from a retrospective review of the cause of death. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2003; 18:977–82. - PubMed
-
- Brown MC, Simpson K, Kerssens JJ, Mactier RA. Peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis rates and outcomes in a national cohort are not improving in the post-millennium (2000-2007). Perit Dial Int 2011; 31:639–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

