The Trio Trial - A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial Evaluating the Effect of a Biocompatible Peritoneal Dialysis Solution on Residual Renal Function
- PMID: 27282852
- PMCID: PMC5033628
- DOI: 10.3747/pdi.2015.00090
The Trio Trial - A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial Evaluating the Effect of a Biocompatible Peritoneal Dialysis Solution on Residual Renal Function
Abstract
♦
Background and objective: Residual renal function (RRF) correlates with mortality and morbidity rates in patients receiving peritoneal dialysis (PD). We examined the effect of a biocompatible PD solution (Gambrosol Trio; Gambro Lundia AB, Lund, Sweden) with lower concentrations of glucose degradation products on rates of decline in RRF. ♦
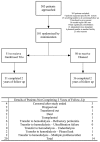
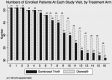
Design, setting, participants, and measurements: Incident patients at 2 centers in Canada and 1 in Hong Kong were randomized (by minimization) in an open-label parallel group trial to receive Gambrosol Trio or standard PD solution (Dianeal; Baxter Healthcare, Mississauga, Canada) for 2 years. Primary outcome was slope of RRF. Secondary outcomes were urine volumes, fluid and nutrition indices, PD and membrane characteristics, peritonitis rates, adverse events, and PD technique survival. ♦
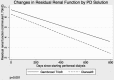
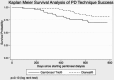
Results: Residual renal function declined by 0.132 mL/minute/1.73 m(2)/month in 51 patients allocated to biocompatible, and 0.174 mL/minute/1.73 m(2)/month in 50 patients allocated to standard PD solution (difference 0.042 mL/minute/1.73 m(2)/month, p = 0.001). Urine volume, body mass index, normalized protein catabolic rates, and fat mass were higher; total body water, peritoneal ultrafiltration, and D/P creatinine did not differ; and serum phosphate, rates of icodextrin, and automated cycler use were lower with Gambrosol Trio use. There were more peritonitis events with Gambrosol Trio use, while PD technique survival did not differ between groups. ♦
Conclusions: The use of the biocompatible PD solution Gambrosol Trio was associated with slower rates of decline in RRF, fluid and nutrition benefits, and increased peritonitis rates.
Trial number: ISRCTN26252543.
Keywords: Peritoneal dialysis; biocompatible PD solutions; peritonitis; residual renal function.
Copyright © 2016 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis.
Figures

References
-
- Perl J, Bargman JM. The importance of residual kidney function for patients on dialysis: a critical review. Am J Kidney Dis 2009; 53:1068–81. - PubMed
-
- Diaz-Buxo JA, White SA, Himmele R. The importance of residual renal function in peritoneal dialysis patients. Adv Perit Dial 2013; 29:19–24. - PubMed
-
- Jansen MA, Termorshuizen F, Korevaar JC, Dekker FW, Boeschoten E, Krediet RT, NECOSAD Study Group Predictors of survival in anuric peritoneal dialysis patients. Kidney Int 2005; 68:1199–205. - PubMed
-
- Cho Y, Johnson DW, Badve SV, Craig JC, Strippoli GF, Wiggins KJ. The impact of neutral-pH peritoneal dialysates with reduced glucose degradation products on clinical outcomes in peritoneal dialysis patients. Kidney Int 2013; 84:969–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

