Clinicopathological features of acute kidney injury associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors
- PMID: 27282937
- PMCID: PMC4983464
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.04.008
Clinicopathological features of acute kidney injury associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors
Abstract
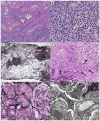
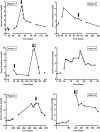
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (CPIs), monoclonal antibodies that target inhibitory receptors expressed on T cells, represent an emerging class of immunotherapy used in treating solid organ and hematologic malignancies. We describe the clinical and histologic features of 13 patients with CPI-induced acute kidney injury (AKI) who underwent kidney biopsy. Median time from initiation of a CPI to AKI was 91 (range, 21 to 245) days. Pyuria was present in 8 patients, and the median urine protein to creatinine ratio was 0.48 (range, 0.12 to 0.98) g/g. An extrarenal immune-related adverse event occurred prior to the onset of AKI in 7 patients. Median peak serum creatinine was 4.5 (interquartile range, 3.6-7.3) mg/dl with 4 patients requiring hemodialysis. The prevalent pathologic lesion was acute tubulointerstitial nephritis in 12 patients, with 3 having granulomatous features, and 1 thrombotic microangiopathy. Among the 12 patients with acute tubulointerstitial nephritis, 10 received treatment with glucocorticoids, resulting in complete or partial improvement in renal function in 2 and 7 patients, respectively. However, the 2 patients with acute tubulointerstitial nephritis not given glucocorticoids had no improvement in renal function. Thus, CPI-induced AKI is a new entity that presents with clinical and histologic features similar to other causes of drug-induced acute tubulointerstitial nephritis, though with a longer latency period. Glucocorticoids appear to be a potentially effective treatment strategy. Hence, AKI due to CPIs may be caused by a unique mechanism of action linked to reprogramming of the immune system, leading to loss of tolerance.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; ipilimumab; nivolumab; pembrolizumab.
Copyright © 2016 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


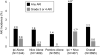
References
-
- Zha Y, Blank C, Gajewski TF. Negative regulation of T-cell function by PD-1. Crit Rev Immunol. 2004;24:229–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

